Dependency Manager
Javapackage: com.etendoerp.dependencymanager
Overview
With this development, the user can have access to all the available dependencies to add, configure them and check information about versions, validations, etc. This is done through two windows: Module Management and Dependency Management.
Module Management
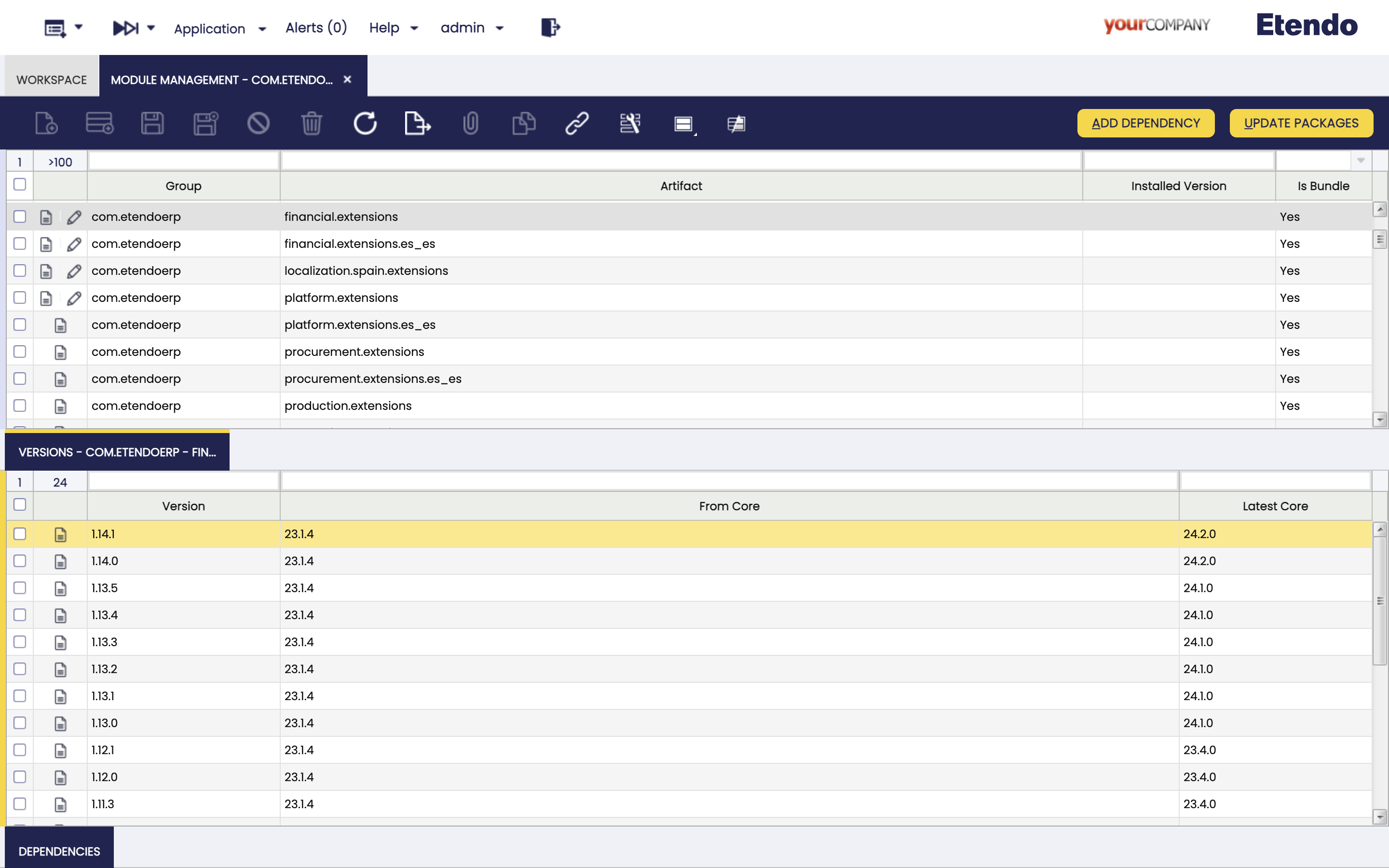
In the Application > Etendo Dependencies Management > Module Management window, the user can see all the modules to be added and select the corresponding version in the versions tab. Once one of the versions is selected, the dependencies of such version can be found in the dependencies subtab.
Info
The fields in this window are read-only.
Fields to note:
- Active: Checkbox to select if this module is active or not.
- Group: the identifier of the artifact.
- Artifact: the unit of deployment fetched and used.
- Installed Version: the version of the module if it is installed.
- Is bundle: Field to filter if this module is a bundle or not.
This window presents two buttons that can be used: Add dependency and Update Packages.
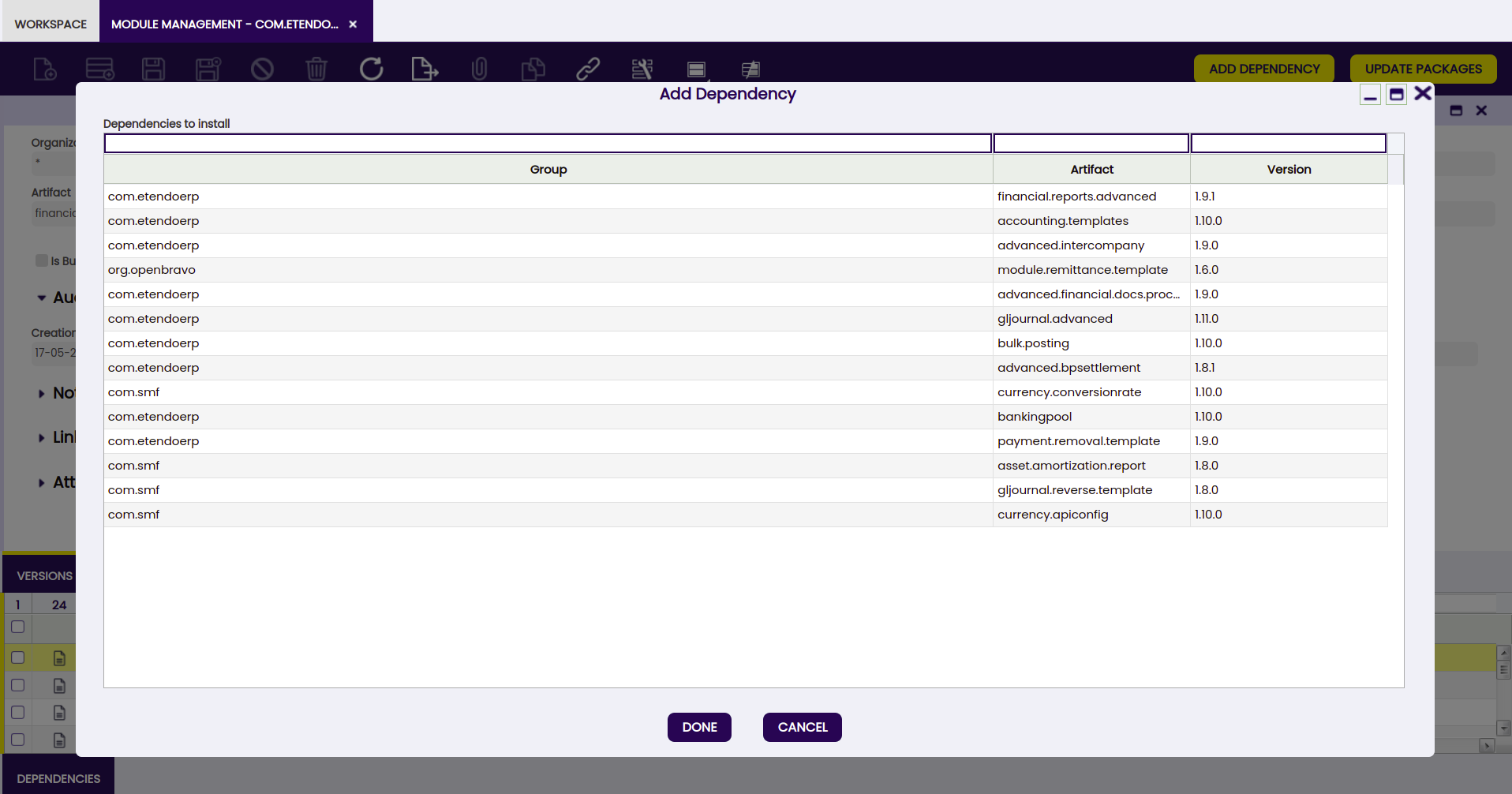
Add Dependency
This button is used to add all the dependecies part of a specific version of the selected module. The popup window shows all the dependencies to be installed.
Note
A warning notification is shown to inform the user about versions compatibility before installing the dependencies shown.
Once the process is done, the Dependency Management window is opened and all the installed dependencies are shown.
Info
In case of executing the process with a bundle, all its dependencies will be added but not itself.
Update Packages
This button is used to execute the Update Packages process which updates the list of available packages with the latest information.
Dependency Management
In the Application > Etendo Dependencies Management > Dependency Management window, the user can find all the dependencies installed in the previous step.
Fields to note:
- Active: Checkbox to select if this dependency is active or not
- Group: The identifier of the artifact.
- Artifact: The unit of deployment fetched and used.
- Version: Version of the module
- Format: Describes the dependency format. They can be
Source,JARorlocal.Source: In this case, the source code is available, to download the dependencies the user must excecute the./gradlew expandModulesGradle task and then compilation is required.JAR: In this case, a standard format for java packages distribution, these include the compiled Java classes, and the dependencies resolution is dynamic.Local: The local format implies that the module is installed but it is not declared as a repository dependency.
- Installation Status: It describes the dependency current status.
- Pending download: This is the status by default when a new dependency is added or updated. To be installed, it is necessary to compile the environment and, in such case, the dependency is in
sourceformat. - Installed: Used once the dependency is already installed.
- Pending download: This is the status by default when a new dependency is added or updated. To be installed, it is necessary to compile the environment and, in such case, the dependency is in
- Version Status: It describes the dependency version status.
- Untracked: Only for external dependencies.
- Update Available: In case there are new available versions.
- Updated: The latest available version is installed.
- External Dependency (Only available for
JARdependencies): Checkbox that identify an external library or module required by the project, managed by Gradle. These dependencies are retrieved from remote repositories during the build process.
This window presents to buttons that can be used: Change Version and Change Format.
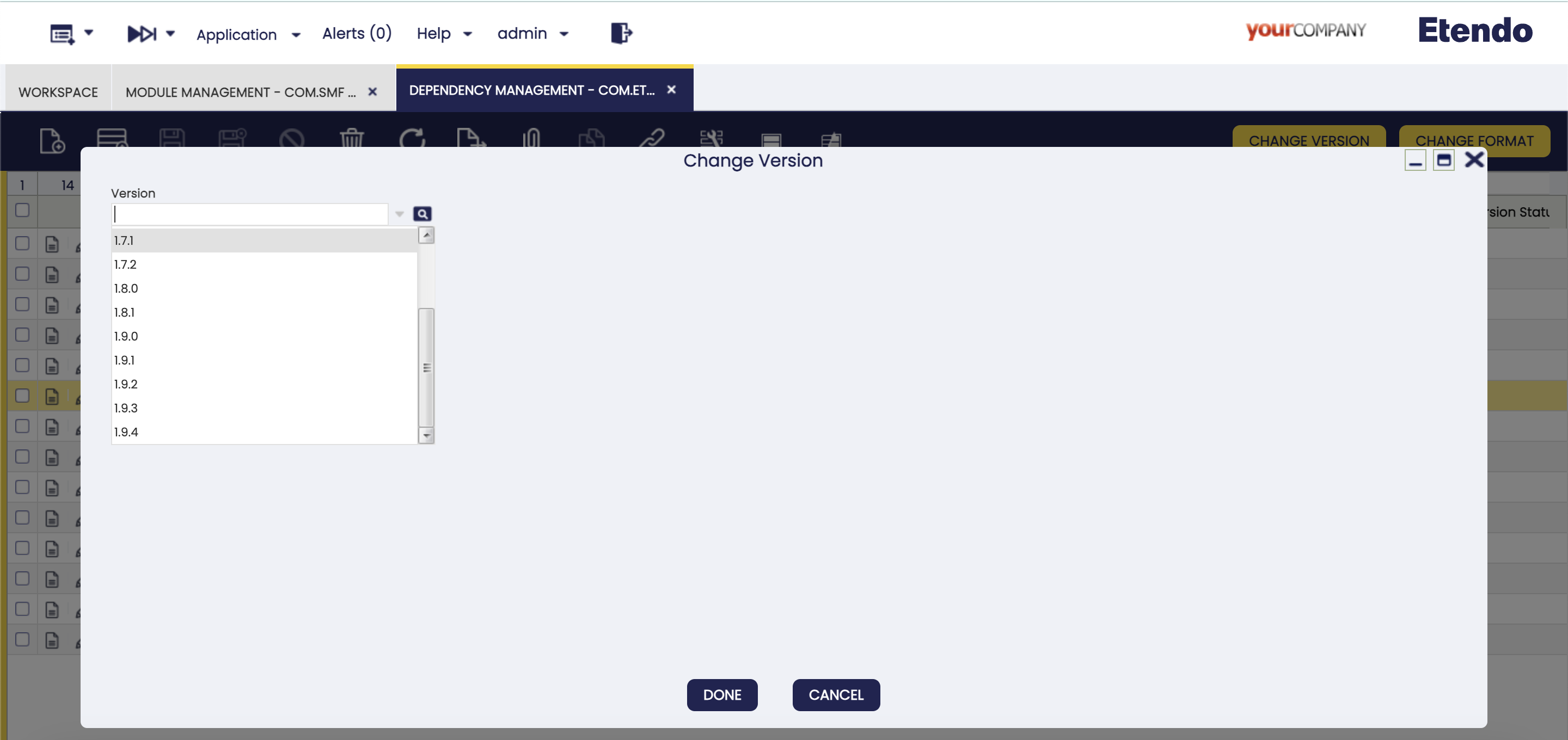
Change Version
This button is used to update or downgrade versions.
When the version of a module is modified, its related dependencies could be modified as well. In this case, it is possible to add new, update or delete versions.
Note
A warning notification is shown to inform the user about versions compatibility before executing the process.
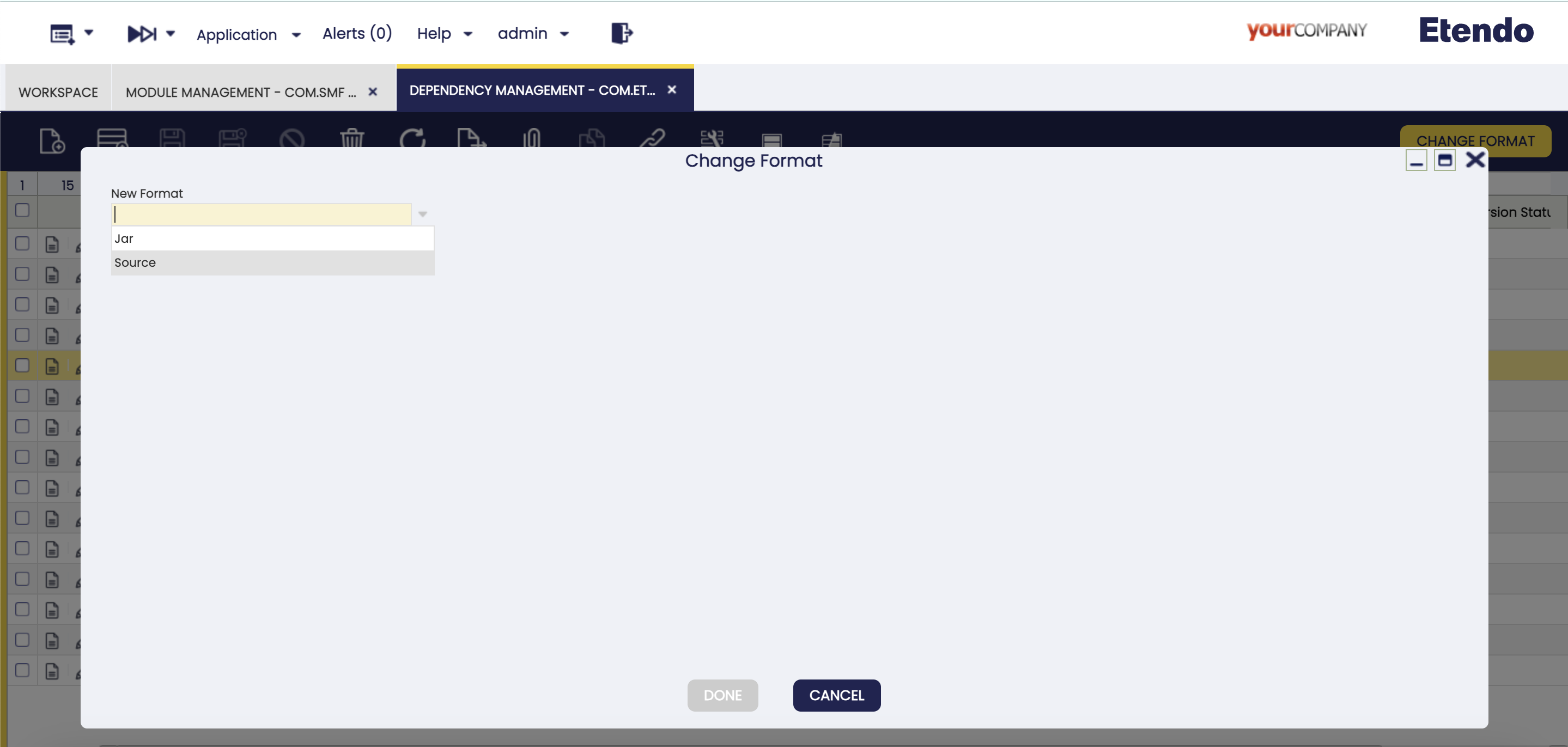
Change Format
This button is used to change the format of the module. This process needs to be executed when it is necessary to migrate from a local format to a gradle dependency, while keeping the modules updated. The options are source, JAR or local.
-
In case the module is originally in
localformat, the options in the Change format popup window areJARorsource. -
In case the module is originally in
sourceformat, the only option in the Change format popup window isJAR. -
In case the module is originally in
JARformat, the only option in the Change format popup window is source. In this case, the window shows a warning notification to remind the user that the original directory is deleted once the process is finished.
Delete Packages
In case you need to remove a dependency to actually complete the action, the environment must be compiled. Also, note that both Source and Local dependencies must be manually removed from the /modules folder prior to compilation.
Add Local Dependencies
This process, in Application > Etendo Dependencies Management > Add Local dependencies, also part of the Etendo Dependencies Management, is in charge of identifying all the locally installed modules without related dependencies, add them to the Dependency Management window with the local format.
Note
The main objective of this process is to add the dependencies in local format, so that in case of being distributed as an Etendo module it can be easily migrated to Sources or Jar format.
Update Packages Information
Since the information about packages is updated frequently, the user can execute this process, in Application > Etendo Dependencies Management > Update Packages Information to update the list of packages with the latest information.
Info
The same process can be executed from the Module Management window, selecting one record and clicking the Update packages button.
Note
Each time the server is restarted, the update process is executed automatically.