Etendo Release Cycle
The launch phase covers all the steps that are necessary to deliver a successful release to the market, including (but not limited to):
- quality assurance testing (QA)
- early adopters testing (Innovators program)
- and training
Etendo solutions are released on a quarterly basis.
- YX is the year and QZ the quarter of the year.
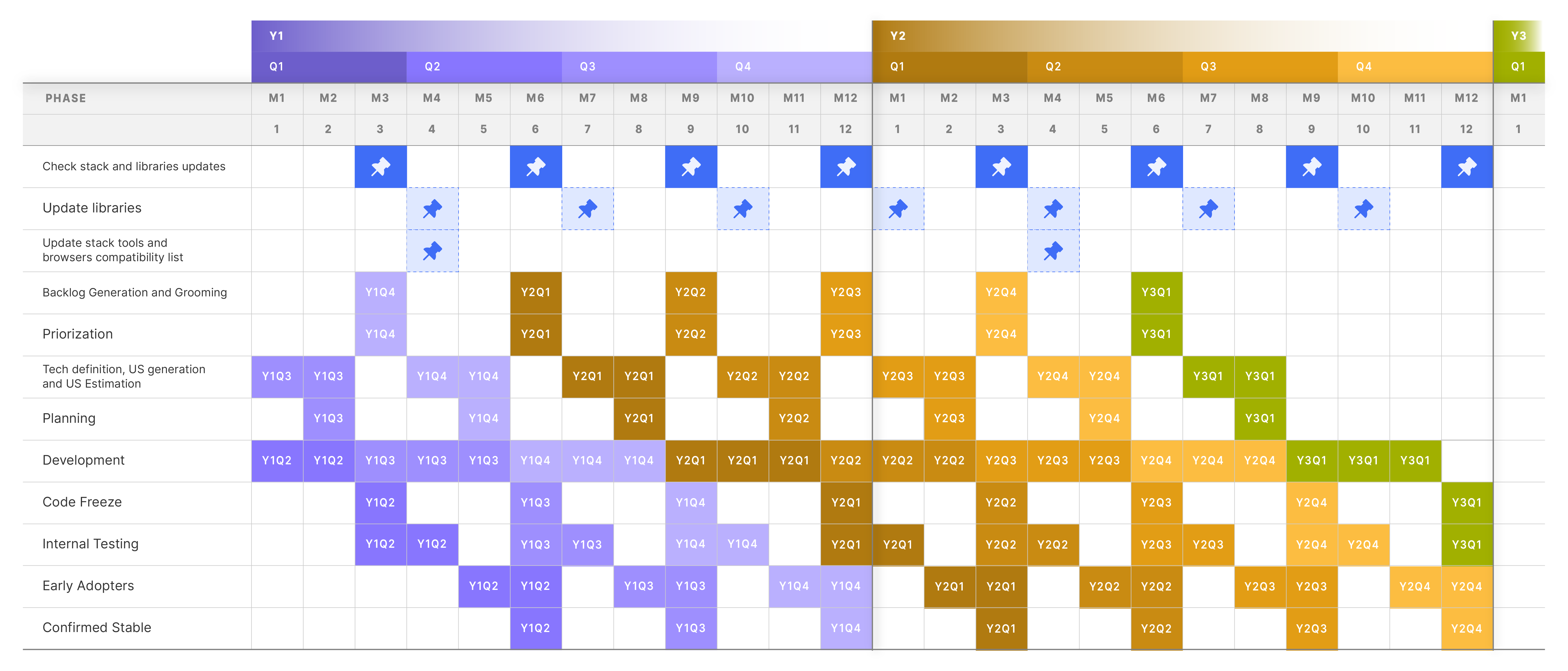
As shown in the image above, the duration of a release cycle is nine months. For instance, and in the case of Etendo Y1Q4 development activities started dated on July and will finish at release dated on March.
Release Phases
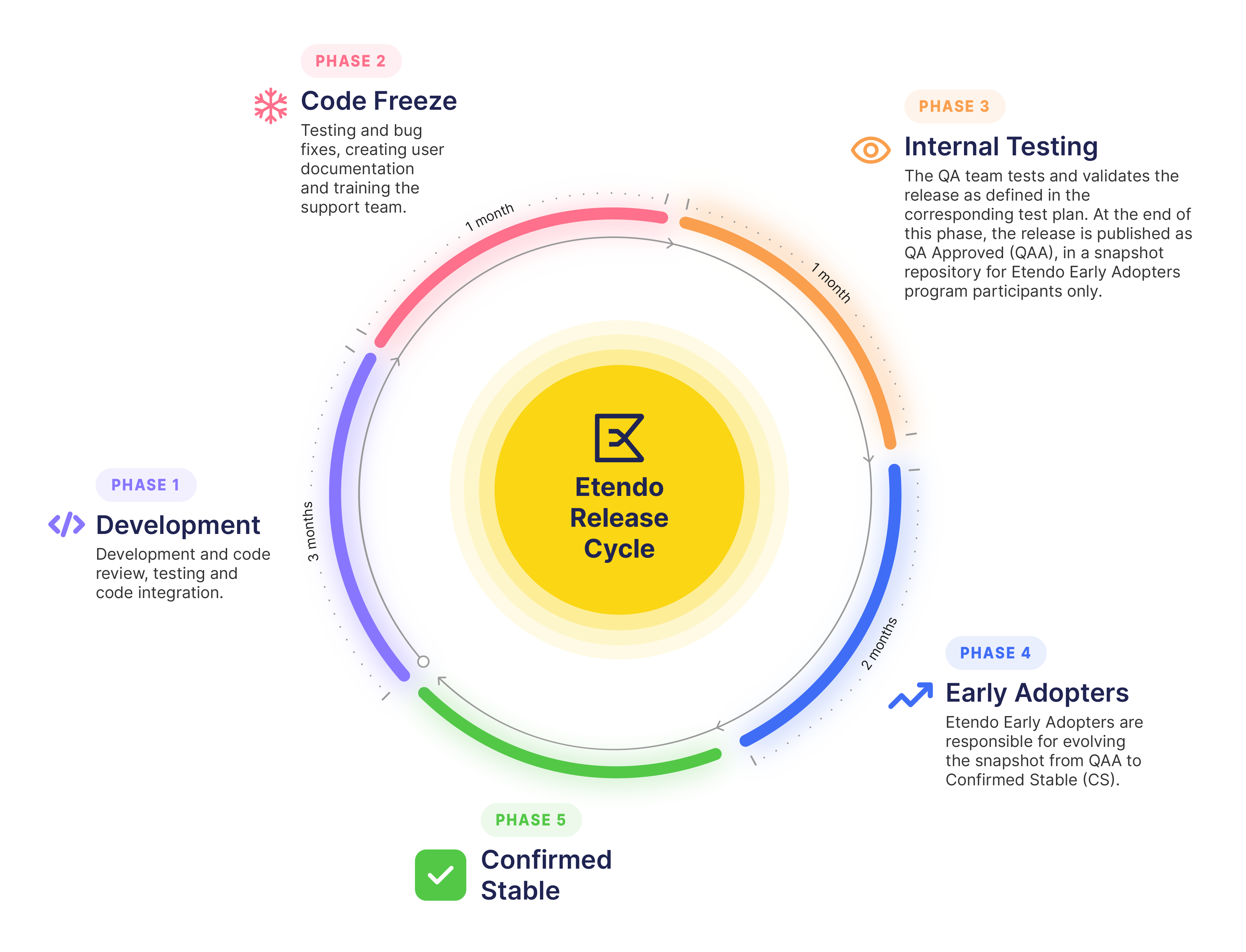
The release process consists of the following phases:
- 3-month development cycle: The engineering team focuses on code development, review, testing, and integration.
- 3-month QA cycle: The QA team tests and validates the release according to the Test Plan, creates user documentation, and trains the support team.
- 3-month Etendo Early Adopters Program: The release is initially published as QA Approved (QAA). This phase includes a maturation cycle to evolve the release from QA Approved (QAA) to Confirmed Stable (CS).
Note
Etendo strongly recommends that only releases that have reached CS are used in production environments.
In summary, Etendo will release Confirmed Stable (CS) releases in March, June, September, and December on a yearly basis.
Info
Etendo will give support to the current year and prior year releases.
Early Adopters Testing (Innovators Program)
As already mentioned, Etendo has established an innovators program based on a maturation cycle to evolve Etendo releases from QAA to Confirmed Stable, in collaboration with a set of Etendo end clients.
These clients install the releases in QAA status for them to use it and help Etendo to mature it.
QAA releases have passed automated tests, all fixed issues have been individually verified and the QA team has completed a set of manual tests to identify further improvement.
When it reaches the QAA stage, the release is not yet available for a wide audience but it can already be used for production purposes for those who have a particular interest, explicitly assuring full alignment with the end client.
As part of the Innovators program, interested Partners will receive support in the update process of a customer’s production environment to the current QA Approved release.
Emergency Releases
When required, there are out of schedule emergency releases which are used for targeted fixing of very important bugs. These bugs may have been reported by our partners, members of the development team or simply bugs found by our automations that are periodically testing our products.
Those releases can be identified by their version which is constructed as follows ETXXQY.Z, where :
- XX is the year of the base release
- QY is the quarter of the base release
- Z is a minor digit number starting with 1
and will run through the same maturity status and release process.
Quality Assurance
In Etendo, we carry out constant processes to ensure the quality and safety of our product throughout the entire development cycle. The following are the main steps of our quality assurance process.
Code Analysis
When code changes or additions are made, the code is subjected to a thorough analysis using the following tools:
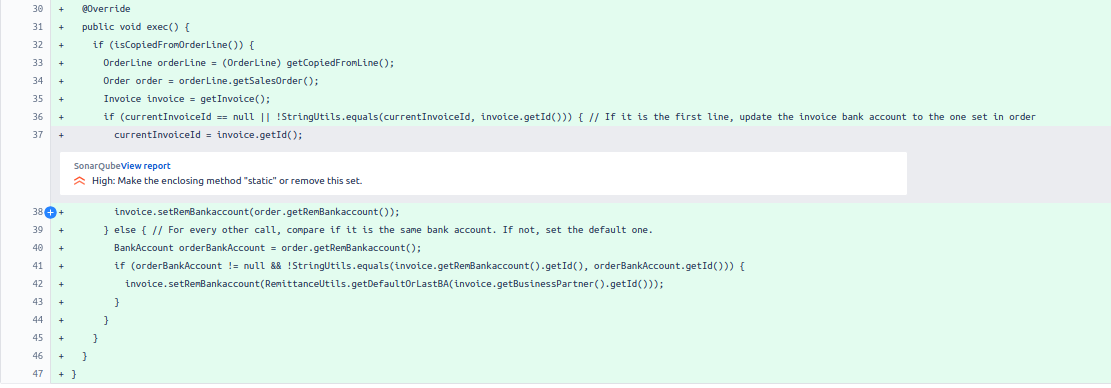
- Sonar: Our development repositories employ Sonar rules to analyze code in pull requests created or updated. Sonar identifies potential problems and makes suggestions to improve code quality.
- Auto Code Reviewer: We have developed a tool called Auto Code Reviewer, which uses ChatGPT to analyze the changes made in the Pull Request and make suggestions. This tool complements the Sonar analysis and helps us to maintain high quality standards in our code and architecture.
Automated Testing
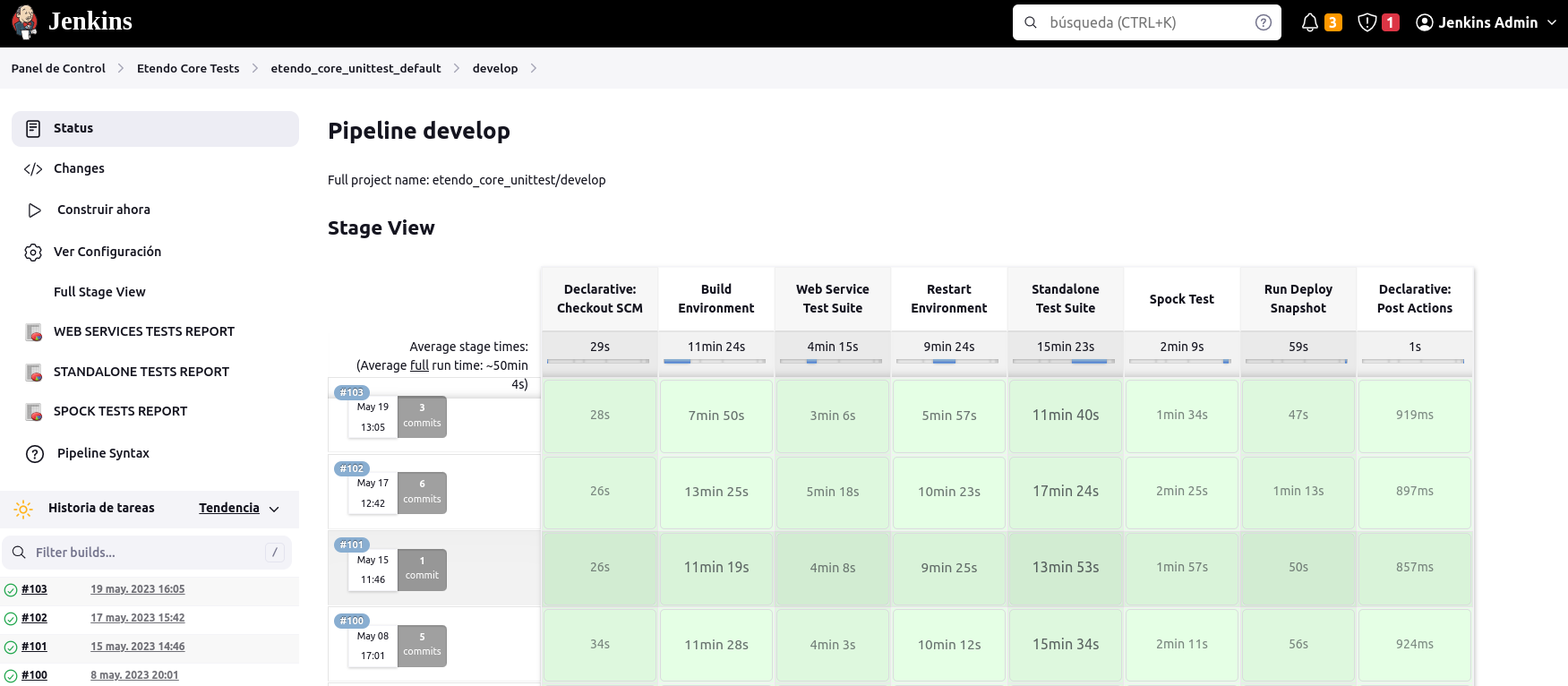
Once a pull request has been created or updated, automated tests are run using Jenkins, our continuous integration system. Through a scheduled job in Jenkins, the following types of tests are executed:
- Compilation Tests: At this stage, we test that the code is compiled correctly, identifying possible errors at compile time.
- Unit Test: We run automated tests designed to verify the behavior and functionality of individual units of code. These tests help us to identify bugs and ensure the correct functioning of the different parts of the system.
If bugs are detected in any of these automated tests, the development team is immediately notified so that they can address and correct them.
Once a pull request has passed the code review and quality assurance processes specific to each development, the merge to the "develop" branch is performed. At this point, automated tests are re-run to ensure that the code integration has not introduced new problems.
Along the lines of the automatic tests that are performed, we have the stress and interface tests that are performed monthly:
- Stress Testing: In addition to the regular automated tests, we conduct stress tests on our applications on a monthly basis. These tests help us identify potential bottlenecks, resource limitations, and areas that may cause degradation or failures under high user loads. By simulating concurrent user interactions and generating high traffic, we evaluate the system's responsiveness, scalability, and overall robustness. Performing these tests monthly ensures that our applications can handle increasing user demands and maintain optimal performance.
- Selenium Interface Testing: To ensure the functionality and user experience of our applications, we conduct monthly Selenium interface testing. Selenium allows us to automate browser interactions and perform tests on different web browsers, such as Firefox and Google Chrome. Using Selenium, we create test scripts that simulate user actions, navigate through the application's interface, and verify that all elements and features work as expected. This ensures consistency across different browsers and helps us identify any compatibility issues that may arise. Conducting these tests monthly allows us to catch any potential interface issues and ensure a seamless user experience across various platforms.
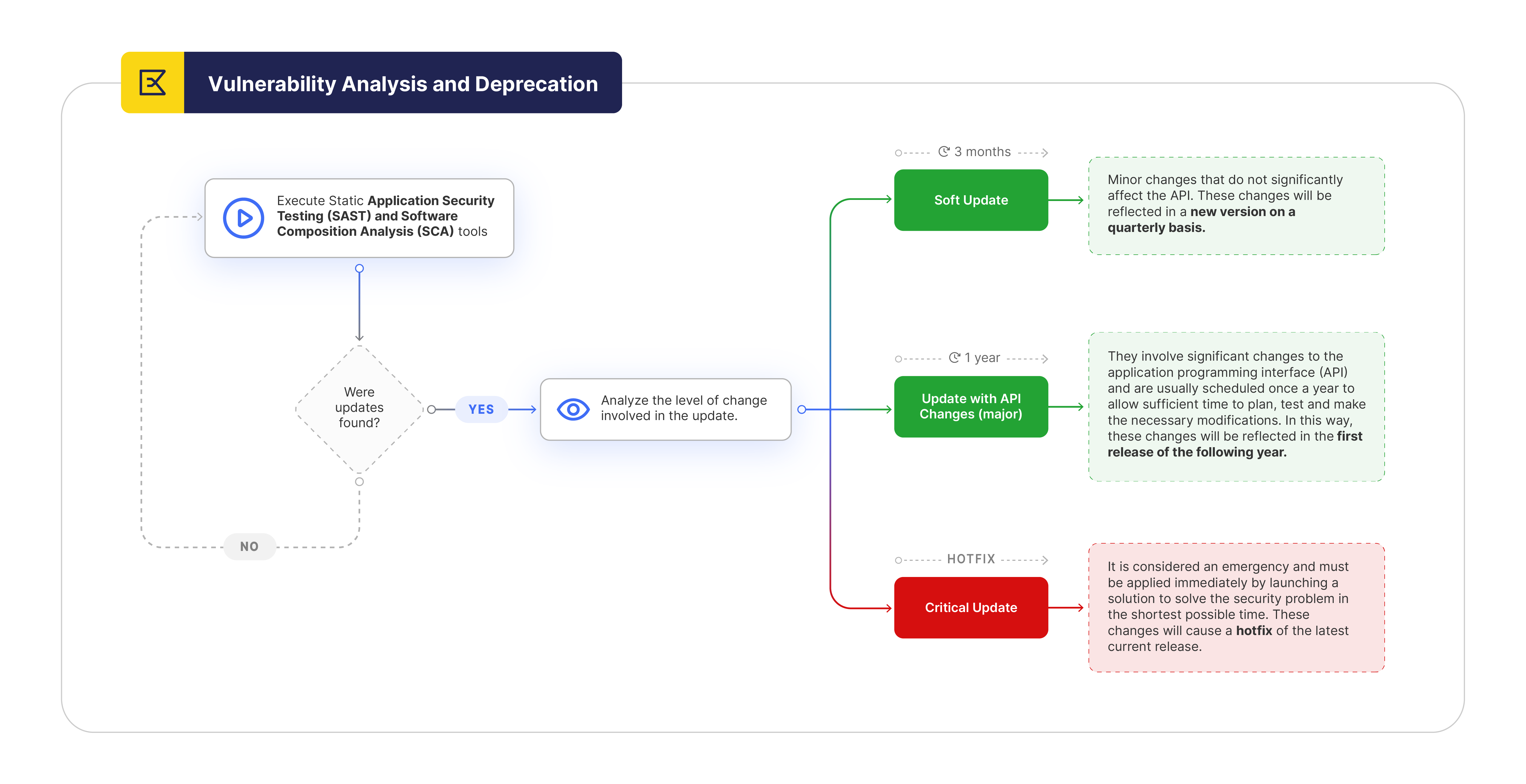
Vulnerability Analysis and Deprecation
On a quarterly basis, we run a Static Application Security Testing (SAST) and Software Composition Analysis (SCA) tools to detect possible vulnerabilities or deprecations in the libraries and stack we use. This analysis allows us to keep our application updated and secure. Based on the results of this tool, we start the corresponding update process, considering the priority level assigned to each identified change.
- Update with API Changes (major): This type of upgrade involves significant changes to the application programming interface (API). A major upgrade generally involves substantial modifications to the way system components or modules interact with each other, which may require extensive changes to existing code to make it compatible with the new version. These changes may include the introduction of new functionality, removal of obsolete features, changes to the data structure or communication protocols. Due to the nature of these changes, a major upgrade is scheduled once a year to allow sufficient time to plan, test and make the necessary modifications to the code and systems using the updated API.
- Soft Update: In a soft update, the changes made are minor, not significant to the API and generally focused on performance improvements, bug fixes, optimizing existing code or updating external dependencies. These changes are less disruptive and can be implemented more frequently, so a soft upgrade is performed quarterly to keep the system up to date and take advantage of continuous improvements. Although the changes are not drastic, extensive testing is still recommended to ensure stability and compatibility with dependencies and related components.
- CRITICAL Update: A critical update addresses a major security vulnerability or issue that could be exploited by attackers to compromise the integrity, confidentiality or availability of the system. This type of update is considered an emergency and must be implemented quickly by releasing a hotfix to resolve the security issue in the shortest time possible. Critical updates may include security patches, workarounds or mitigations to prevent exploitation of the vulnerability while a more complete solution is being worked on.
Integration of Snyk in Vulnerability Analysis
 At Etendo, we are committed to ensuring the security of our applications at all times. That's why one of the prominent tools we use is Snyk, a powerful Software Composition Analysis (SCA) solution.
At Etendo, we are committed to ensuring the security of our applications at all times. That's why one of the prominent tools we use is Snyk, a powerful Software Composition Analysis (SCA) solution.
Snyk enables us to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the libraries and dependencies used in our application stack. By integrating our repositories with Snyk, we gain detailed visibility into potential vulnerabilities and deprecations that may exist in our code.
Snyk is widely recognized for its ability to accurately and promptly identify vulnerabilities in software dependencies. Through Snyk, we can perform continuous and real-time analysis of our dependencies, enabling us to detect any security issues early on and take proactive measures to address them.
The integration with Snyk provides us with detailed information on each identified vulnerability or deprecation, including descriptions, severity levels, and specific recommendations for resolution. This information is invaluable as it allows us to assess and prioritize the necessary changes based on their potential impact on our application.
Based on the analysis results from Snyk and other security tools, we initiate the corresponding update process, considering the assigned priority level for each identified change. This approach enables us to effectively manage security risks and keep our application up to date and secure for our users.
Etendo Release Notes
Every time Etendo releases a new version, all that it contains is documented in the corresponding Release Notes wiki page.
It is important to highlight that within Etendo release notes wiki page, there are direct links to what a given release includes.
New versions of Etendo can include:
- new functionalities implemented according to the corresponding product roadmap,
- fixes of the issues reported by Etendo partners, fixed by Etendo according to the corresponding Etendo partner’s services level agreement,
- and extensions, modules which extend the functionality of Etendo.
This work is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.5 ES by Futit Services S.L.