How to Configure Log
Overview
Logging allows developers to record messages during code execution. Use these messages to diagnose backend issues such as errors, warnings, and performance bottlenecks.
To learn how to use logging in your custom code, refer to the How To Log Using Log4j guide.
Configuration
Logging is configured using three main configuration files, depending on the scenario:
config/log4j2.xml: Configuration for command-line build tasks (e.g.,./gradlew install).config/log4j2-web.xml: Configuration for the Web Application running in a container like Tomcat.src-test/src/log4j2-test.xml: Configuration used specifically for JUnit tests and suites.
File
By default, log output is redirected to a file. This is defined by the <RollingFile> tag inside the <Appenders> section. The defaults are:
<RollingFile name="RollingFile" fileName="${logDir}/etendo.log"
filePattern="${logDir}/etendo-%d{yyyyMMdd}-%i.log.gz">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d [%t] %-5p %c - %m%n"/>
<Policies>
<TimeBasedTriggeringPolicy />
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="100MB" />
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="30"/>
</RollingFile>
etendo.log within the ${logDir} directory. In a standard Tomcat deployment, this directory is typically found in the logs/ folder of the Tomcat installation.
Tip
If you are running Etendo from the command line, ${logDir} usually points to the build/ directory or the project root depending on the task execution.
Console Logging
You can also see logs in the console (Standard Output) by using the <AppenderRef ref="Console"/> appender. This is useful for development to avoid constantly tailing a file.
<Loggers>
<Root level="info">
<AppenderRef ref="RollingFile"/>
<AppenderRef ref="Console"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
....
<Appenders>
<Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d [%t] %-5p %c - %m%n"/>
</Console>
...
</Appenders>
Log Verbosity
Verbosity is controlled by log levels: ALL, TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, and OFF.
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| ALL | All levels, including custom ones. |
| TRACE | Extremely fine-grained informational events, more detailed than DEBUG. |
| DEBUG | Fine-grained informational events most useful for debugging applications. |
| INFO | Informational messages highlighting application progress at a high level. |
| WARN | Potentially harmful situations. |
| ERROR | Error events that might allow the application to continue running. |
| FATAL | Severe error events that will likely lead to application failure. |
| OFF | No log messages. |
Production environments
Avoid using DEBUG or TRACE levels in production environments, as they can significantly impact performance and consume large amounts of disk space.
It is possible to configure the log level globally or per class/package.
This can be modified in two ways:
-
Static Configuration: Edit the
log4j2*.xmlfiles. This requires a redeploy (./gradlew smartbuild) and a Tomcat restart to take effect.-
Globally: Change the Root Logger level:
-
Per Java class or package: Add a
<Logger>entry:<Loggers> ... <!-- Set a specific package to debug level --> <Logger name="com.etendoerp.copilot" level="debug"/> ... </Loggers>Note
These loggers inherit appenders from the Root logger by default. To change this, set the
additivityattribute tofalse.Info
For more information, see the Log4j2 documentation.
-
-
Runtime Configuration: This method does not require a restart but is non-persistent (settings are lost after a Tomcat restart). To modify levels at runtime:
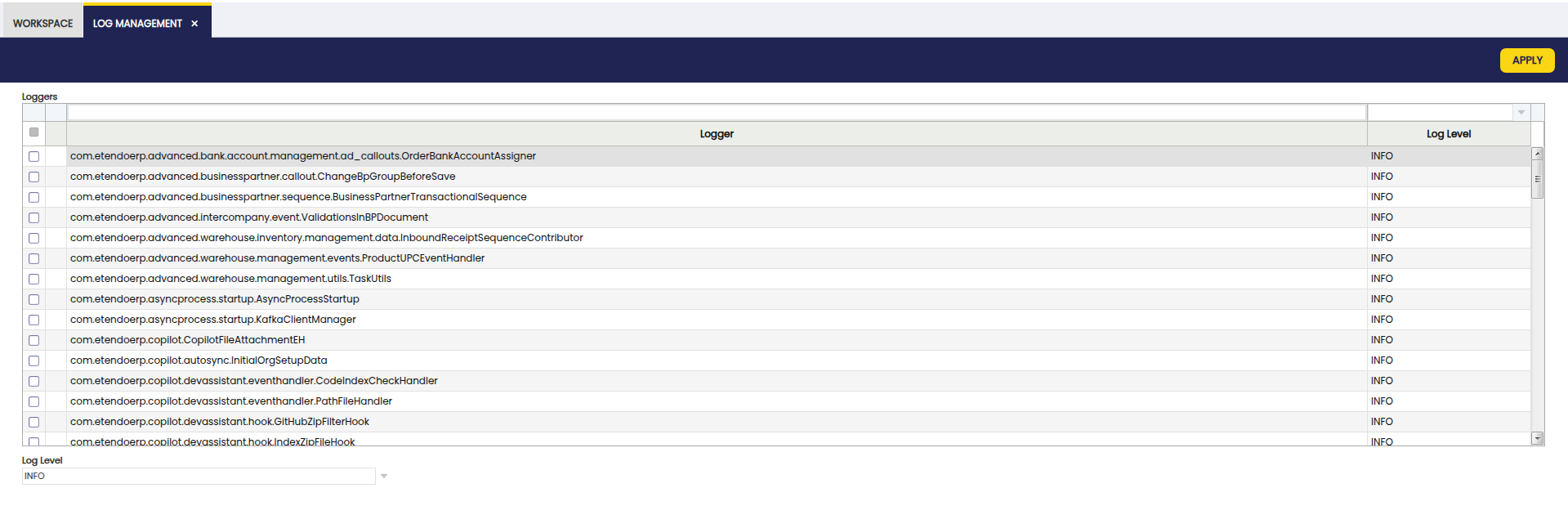
- Log into the application as System Administrator.
- Navigate to
General Setup > Application > Log Management. - Filter and select the desired loggers.
- Choose the log level to set and click Apply.
Info
Loggers for classes or packages appear in this list as they are executed. If a specific logger is missing, run the functionality that uses it to register it in the system. Note that restarting Tomcat clears this list, and you will need to re-run the features to see the loggers again. For debugging during application startup, configure the log level directly in log4j2-web.xml.
Rotation
To prevent log files from growing indefinitely, rotation is configured to archive old logs.
Configuration is handled in the <RollingFile> section:
<Policies>
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="100MB" />
<TimeBasedTriggeringPolicy />
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="30">
<Delete basePath="${logDir}">
<IfFileName glob="etendo-*.log.gz">
<IfAccumulatedFileCount exceeds="30"/>
</IfFileName>
</Delete>
</DefaultRolloverStrategy>
By default, the log file is limited to 100MB. It is archived and compressed daily or when it reaches the size limit. Up to 30 archived files are kept; once this limit is reached, the oldest archive is deleted.
This work is a derivative of How to Configure Log by Openbravo Wiki, used under CC BY-SA 2.5 ES. This work is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.5 by Etendo.