Etendo Gradle Plugin
Overview
This article explains how to use Gradle, an open-source build automation tool that is designed to be flexible enough to build almost any type of software.
Note
For additional information read: What is gradle?.
Etendo uses Gradle to define and improve compilation, version management, modules publication, migrations and more tasks.
How to use Gradle
Etendo project includes an embedded wrapper from Gradle called gradlew. Run the following command in the Etendo project directory, and it will execute the mentioned task.
You can use -P<Parameter Name> to pass parameters in a task. For example:
Common Gradle flags
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
--offline |
To execute Gradle without internet connection. |
--stop |
To stop all Gradle daemons. |
--no-daemon |
To execute a Gradle task without launching a daemon. |
--info |
To give more information in the task execution. |
--refresh-dependencies |
Will force download of dependencies. |
Etendo Plugin
Add in the build.gradle file the plugin version available in Gradle Plugin Release Notes.
Plugin Configuration
The plugin configuration needs to be declared in the build.gradle file in etendo block.
In the following sections, you can find all the flags or variables available to set up and a brief description of each one.
etendo {
/**
* Flags used to indicate if the 'default' core dependencies (jar files) should be
* loaded (This is the case when you are working with sources and the 'default' jar files are missing)
* This flags should be false.
*/
boolean loadCompilationDependencies = false
boolean loadTestDependencies = false
/**
* Flag used to ignore loading the source modules to perform resolution conflicts.
* Default true
*/
boolean ignoreSourceModulesResolution = true
/**
* Flag used to perform or not the resolution of conflicts.
* Default true
*/
boolean performResolutionConflicts = true
/**
* Flag used to ignore throwing a error if there is conflict resolutions with the Core dependency.
* Default false
*/
boolean forceResolution = false
/**
* Flag used to apply the subproject dependencies to the main project.
* Default true
*/
boolean applyDependenciesToMainProject = true
/**
* Flag used to prevent overwriting the transitive source modules when performing the expandModules task.
* Default true
*/
boolean overwriteTransitiveExpandModules = true
/**
* Flag used to exclude the Core dependency from each subproject to all the configurations.
* Default true
*/
boolean excludeCoreDependencyFromSubprojectConfigurations = true
/**
* Flag used to indicate that the current Core version support jars.
* Default true.
* When this flag is set to false, the behavior of the 'expandModules' task will change, forcing to expand all the declared modules with 'moduleDeps' to sources.
*/
boolean supportJars = true
/**
* List of Etendo artifacts to always extract and ignore from the version consistency verification.
*/
List<String> ignoredArtifacts = []
/**
* Flag use to prevent throwing error on version inconsistency between modules.
* Default false
*/
boolean ignoreConsistencyVerification = false
/**
* Flag used to prevent throwing error when an artifact could not be resolved.
* This includes transitives ones.
* Default false
*/
boolean ignoreUnresolvedArtifacts = false
/**
* The list of modules that should not be re expanded.
* Default empty.
*/
List<String> sourceModulesInDevelopment = []
/**
* Flag used to ignore the Etendo CORE jar dependency located in the
* build.gradle of the root project.
* Default false.
*/
boolean ignoreCoreJarDependency = false
}
Main Build Tasks
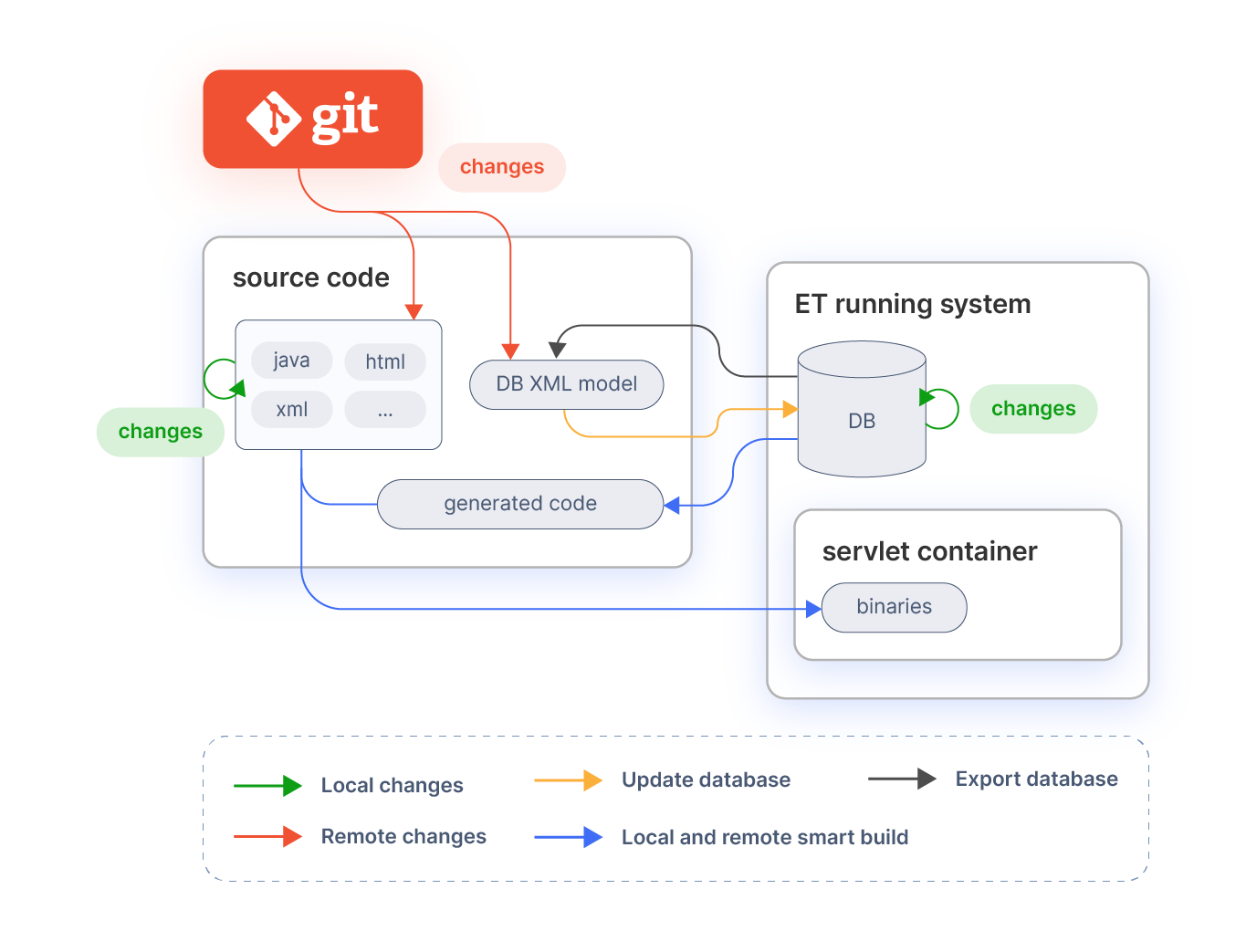
This section explains the main build tasks following the steps as illustrated in the image.
In most of the cases, it is only necessary to use 3 tasks (install , smartbuild and export.database). There are a number of other tasks that can be used but they are not required for the standard process.
Info
For more information, see Detailed Build Tasks section.
The main task for the standard process is smartbuild which performs all the required processes as explained below. This task accepts an optional property:
localfor local or remote developments which by default is set to yes .
The difference between local and remote development is illustrated in the diagram. Local development are changes by the developer him/herself. Remote developments are changes done by other developers. Changes by remote developments are pulled from the source code revision system.
Info
remote means that the user is bringing changes to the workspace from an external location, e.g. with a git pull or ./gradlew expandModules.
Initial installation
After downloading the Etendo ERP source files. It is necessary to install and deploy it. Check our guide about Etendo Install
Database export
In most cases developments include modifications on the database. These modifications can be persisted in xml files using the DBSourceManager tool. DBSourceManager exports to xml files only the modules (including core) that are set as In Development. To export the database execute:
After this step, the changed model xml files can be pushed/committed to the source code revision system, so that other developers can pick them up and continue working on top of it.
When a module is exported using the export.database task, it is first validated to check for common errors. If the validation fails then the export.database task will also fail and export is not possible.
The following checks are currently done:
- A table defined in the Application Dictionary should be present in the database and vice versa.
- Column definitions in the database and the Application Dictionary are compared, any mismatch is reported. The column datatype, default value and length are checked.
- Tables should have a primary key.
- Foreign key fields should be part of a foreign key constraint.
- Names of tables, columns and constraints are checked for their length (Oracle and PostgreSQL has a 30 character limit there).
Update database
Database model changes are distributed by committing the database schema as xml to SCM. Other developers pull the changes from SCM and can apply them to update their own database. After updating the database the process is exactly the same as the local one, that is compile and deploy the elements that have been modified since last build.
All the required actions (update database, compile last modifications and deploy them) can be done with only the smartbuild command:
The only difference with the local development is in the local parameter which makes the process to update the database in case the xml files were changed.
Detailed Build Tasks
This section contains a detailed listing of all available build tasks.
Libraries build tasks
| Task | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
core.lib |
Compiles and generates a .jar file from the src-core project. Which is needed by wad.lib and the rest of build tasks. |
Required by: wad.lib |
wad.lib |
Compiles and generates a .jar file from the src-wad project. Which is needed by the build tasks. This project contains the WAD, the automatic window generator. |
Requires: core.lib, database created Required by: compile.* |
trl.lib |
Compiles and generates a .jar file from the src-trl project. Which is needed by the translate task. This project allows to translate to different languages manual windows. |
Requires: core.lib |
Build tasks
| Task | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
install |
Installs the whole application: creates the database, compiles it and generates a war file to be deployed or copies the classes to Tomcat's directory (depending on the deploy.mode property set in Openbravo.properties). |
Calls: create.database, core.lib, wad.lib, trl.lib, compile.complete.deploy, applyModule. |
smartbuild |
Makes an incremental build of the application. Including: update.database compile deploy All these tasks are done only if needed. |
Requires: Database must be created and populated with data Properties: local: (yes/no default as yes) when this property is set to no update.database task is executed, otherwise it is not executed. tr: (yes/no default as yes) if set to no, translation process is not executed. force: (yes/no default as no) used with local=no. If set to yes it will overwrite the changes in the database with the XML information. Note: All un-exported changes will be lost. |
compile.complete |
Compiles all modified classes (including the generated ones) but before removes all the generated and built files, so the whole application is built | Requires: wad.lib, trl.lib, database created and populated. Calls: translate Properties: tab: specifies the window name(s) to be generated, to specify more than one window add them as a list of comma separated values. Note that even window is specified by this property, its 2.50 code will not be generated unless it is required or forced. tr: if set to "no" it will not call the translation process. module: a list of comma separated javapackages of modules to generate just the windows containing objects for those modules. |
generate.entities |
Generates the Java files for src-gen directory, and compiles them. They are used by DAL to access to the database information. |
Requires: Database must be created and populated with data. |
translate |
Checks in the manual windows User Interface files the translateable elements that have not been yet registered and registers them, this is necessary to be able to translate those interfaces to different languages. | Requires: trl.lib Called by: This task is called by the compile.* tasks in case the tr property is not set to "no". |
antWar |
Generates a war file from the existing built code. In fact it only zips the application in a single war file. | Requires: compile.*: the application must be built before calling this task. |
deploy.context |
Deploy the existing war file in the tomcat context using the tomcat manager. | Requires: war file must be created Tomcat manager must be running These properties must be properly set in the Openbravo.properties file: tomcat.manager. url tomcat.manager.username tomcat.manager.password |
Database tasks
| Task | Description | Notes | Sub Tasks |
|---|---|---|---|
create.database |
Creates the database from the xml files, note that the database is first removed. If the apply.on.create property is set, masterdata and sampledata will be inserted in the database. If not, only sourcedata will be inserted. |
Properties: apply.on.create: If is set to true and there are modules they will be applied, otherwise they will be set as In process status. |
create.database.script: The same as create.database.structure but does not affect the database it only generates the sql script file with all the statements that would be executed by the other tasks. |
update.database |
Synchronizes database with the current database xml files. By default it checks that no changes in application dictionary in database are done, if so the process stops. | Properties: force: (yes/no default as no) Do not check for database modification and update directly. This can cause loss of database data. |
update.database.script: It is the same as update.database.structure but does not modify the database. It only generates a sql script file with the statements that would be executed by the other tasks. |
export.database |
Synchronizes xml files with the database current contents. By default they are only exported in case there are modifications in the database. In addition performs database validations for the modules which are exported. | Properties: force: (yes/no default as no) Forces the export skipping the check of which files had been modified since last update.database. validate.model: (yes/no default as yes) Checks the model that is being exported fulfills a series of rules related to modularity, oracle-postgreSQL compatibility, etc. In case any of these rules is not complied, export will not be done and an error message will be raised. |
Info
update.database and export.database tasks support multi-thread parallel execution for some of their actions such as index creation or function standardization. By default, the number of threads used is calculated as the half of the available number of cores in the machine where the task is executed. This value can be set by adding the -Dmax.threads=numOfThreads parameter.
Test Tasks
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
test |
By default, all Etendo tests are run. You can use the --tests "<package>" to specify which tests you want to run. |
Info
For more information about execution test in Gradle visit Test Filtering in Gradle
Other Tasks
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
migrate.attachments |
Migrates the attachments to the new attachment model. |
Common Gradle Tasks
Danger
Since Etendo Classic 25Q1, all Gradle tasks require Java 17 or higher. To add support for previous versions, the new flag java.version has been added.
This new flag forces the use of Java 11.
-
Creates the properties and configuration files.
Command line parameters Description -PforceDefaultProps=trueRecreates the default properties file from the template. -PforceBackupProps=trueRecreates the backup.properties file from the template. -PforceQuartzProps=trueRecreates the quartz.properties file from the template. -
Creates the properties files from the templates in
/configfolder. The setup tasks depend on this task. -
Creates the database and installs reference data.
-
Compiles the Java classes that were modified and deploys them to Tomcat.
Command line parameter Description PignoreConsistency=trueFlag used to ignore the consistency verification (verifies the versions between the local modules and the installed ones) -
Deletes all the Java Classes and recompiles them.
-
Updates the database applying the changes in XML files.
-
Exports the database changes to XML files
-
Exports the module Application Dictionary data.
-
Exports the configuration script.
-
Task to download core dependency.
Command line parameter Description -PforceExpand=<true>Flag used to force the sources expansion when the core is in JAR. -
Task to download the modules dependencies in sources.
Command line parameter Description -Ppkg=<package name>The name of the module to be re expanded in case that it is already in sources. This will OVERWRITE all the changes in the module. -
Task to delete directories created by the expandCore task.
Modules
-
Creates the
build.gradlefile with all the necessary information to publish.Command line parameters Description -Ppkg=<package name>The name of the module. -Prepo=<repository name>The name of the repository. -
Publish the module to a custom repository.
Command Line Parameters Description -Ppkg=<packagename>Required The name of the module. -PupdateLeaf=trueThis updates automatically the version of the project being published. By default false.
Uninstall Modules (uninstallModule)
Source Modules
To uninstall an Etendo module you need to run the gradle task.
This task will try to delete the source module and the source dependencies which depends on it.
If the module to uninstall is a dependency of other source module, an exception is thrown. You can force the uninstall providing the flag -Pforce=true.
JAR Modules
-
To uninstall a dependency in
JARformat, simply remove the dependency from thebuild.gradlefile and recompile. -
If you want to uninstall a transitive dependency, you can make use of Gradle Exclusion Rules (exclude dependencies) to prevent the extraction of a
JARdependency. In thebuild.gradleof the root project you can specify the dependency to exclude:-
Exclude Dependencies in globaly:
-
Exclude transitive dependencies:
Tip
- You can also make use of Gradle Exclude Rules if the dependency belongs to a source module, apllying the rules in the module
build.gradlefile. - A
JARmodule could also be a transitive dependency. You can see the transitive dependencies tree running the gradle task:./gradlew dependencies --infoand exclude the root parent dependency. - Etendo
JARmodules are dynamically extracted in the root projectbuild/etendo/modulesdirectory.
Finally you need to rebuild the system:
-
Internal Developer Tasks
-
Used to clone all the git submodules of a module extension (bundle). The module
build.gradleshould contain the propertybuild.gradleext.defaultExtensionModules = [ 'git@github.com:example1.git', 'git@github.com:example2.git' ]Command line parameter Description -Ppkg=<package name>Required The name of the bundle -
Creates all the
build.gradlefiles for each module using the database fromAD_MODULE.xml.Command line parameter Description -Ppkg=<package name>Required The name of the module -Prepo=<repository name>Required The name of the repository -Pbundle=<bundle package name>The name of the bundle -Ppkg=allCreates all the build.gradlefiles for each module, eachbuild.gradlefile will contain the dependencies between projects (in the dependencies block). -
Parameters to override the default core group, name and version.
Command line parameters Description -PcoreGroup=<core group>The core group name -PcoreName=<core name>The core name -PcoreVersion=<core version>The core version -
Parameters to override the default repository. Publish all the modules of a bundle in the source modules directory.
Command line parameters Description -Ppkg=<bundle package name>Required The package of the bundle -PupdateLeaf=trueThis updates automatically the version of all the project being published. By default false.-Pupdate=<major, minor, patch>Used to specify which part of the version will be updated. By default patch.-PpushAndTag=trueUsed to specify if the modules published should push the changes and create a tag in the git repository. By default false.-PpushAll=trueUsed to specify if all the modules should run the push and tag. By default false. -
Task used to push and tag the modules' changes.
Command line parameters Description -PpushAll=trueUsed to specify if all the modules should run the push and tag. By default false. -
Updates the version of a dependency in each
build.gradlesubmodule.Warning
If you put a wrong version, you have to revert the changes manually.
Command line parameters Description -Pdependency=<dependency name>The name of the module to update in each build.gradle. Defaultcom.etendoerp.platform.etendo-core-PlowerBound=<version>The lower version bound. Example: -PlowerBound=1.0.3-PlowerBoundInclusive=<true or false>By default false.-PupperBound=<version>The upper version bound. Example: -PupperBound=1.0.3-PupperBoundInclusive=<true or false>By default false.-PexactVersion=<version>Will replace the current version with the specified one. The version should be between quotes. Example: -PexactVersion="[1.0.3]"
Ant Tasks
Most of ant build tasks previously used can be run with Gradle:
Except for some commands:
| Old Command | New Command |
|---|---|
clean |
antClean |
setup |
antSetup |
init |
antInit |
install.source |
antInstall |
war |
antWar |
Conflict Resolution
Note
Etendo makes use of the Conflict Resolution Strategy offered by Gradle.
This approach is used to identify conflict between Etendo artifacts published in a repository.
For example, when you make use of an Etendo module, which depends on the Etendo core
group = 'com.etendoerp'
ext.artifact = "moduleCextract"
version = '1.0.1'
dependencies {
// Etendo CORE dependency
implementation 'com.etendoerp.platform:etendo-core:[22.1.1, 22.1.2]'
}
and you are currently working with the Etendo core in 22.1.0, then a conflict resolution is found.
Depending on the type of conflict, if the problem is with the Etendo Core, then a Exception will be thrown.
To force the dependencies' resolution must be the last step to follow
You can force the resolution using the extension flag
If you want to skip the resolution you can add to the plugin extension the flag.
Version Consistency
The version consistency approach verifies that an extracted Etendo JAR artifact is consistent with the installed one (Equal version).
When a new Etendo JAR dependency is added or the version is updated, an update.database needs to be run before executing any compilation task (smartbuild, compile.complete, etc).
You can force the compilation tasks by adding to the Etendo plugin extension the ignore flag
This section explains how to ignore the consistency verification. Use this approach only if there are no conflicts between versions.
or run the tasks with the-PignoreConsistency=true flag.
By default Etendo does not allow you to add a JAR dependency with an old version to the current installed one. You can ignore this behavior adding the module name to be updated with an old version as a configuration.
Recompile CSS files
Requirements
- Node.js: Version 16 or higher.
- npm: Node Package Manager.
- Sass: Must have a Sass compiler installed.
How to install Node.js, npm and Sass
Node.js 16.10.0 using NVM:
-
Install NVM (Node Version Manager):
Close and reopen your terminal to start using NVM, or execute the following commands: -
Install Node.js version 16.10.0:
Note: If you encounter errors during the installation of Node.js with the
nvm install 16.10.0command, it might be becausecurlisn't installed or is misconfigured on your system. In such cases, you can try running the following commands:After successfully configuring
curlusing this method, return to this guide and execute the steps above to install NVM and set up Node.js. -
Set Node.js version 16.10.0 as the default version:
-
Verify the installation:
Homebrew Installation:
- Install Homebrew by running the following command in the terminal:
- Once Homebrew is installed, verify it by checking its version:
Node.js & npm Installation using Homebrew:
-
Update Homebrew (ensuring you have the latest package definitions):
-
Install Node.js and npm:
-
Verify the installation of Node.js and npm:
Node.js & npm:
-
Download the Node.js Windows Installer from the official website.
-
Run the installer and follow the instructions.
-
After installation, open a command prompt or PowerShell and verify the installation:
Installing npm (Node Package Manager)
If you don't have npm installed on your system, follow these steps:
- Install npm globally using the following command:
- Confirm the installation by checking the versions of node and npm:
Installing Sass (Syntactically Awesome Style Sheets)
If you have npm installed and need the Sass compiler, follow these instructions:
- Use npm to install Sass globally on your system:
- Confirm the Sass installation by running:
Seeing the Sass version number means that Sass has been installed correctly.
Execution
The cssCompile task in the Etendo Gradle configuration is specifically designed to convert .scss files into .css files. To customize the Etendo skin, you will need to work with .scss files.
After executing the task, look for the following output to indicate a successful build:
Successful Execution
After executing the task, the following output indicates a successful build:
This confirms the successful processing of the files.
Finally, restart Tomcat to apply the changes and ensure the updated .css files are properly deployed.
Delete Client Process
The delete.client task allows running the Delete Client Process directly from gradlew. This task also allows running this process with the Tomcat service down to avoid database locks.
| Command line parameters | Description |
|---|---|
-DclientId=<AD_Client_ID> |
AD_Client_ID of AD_Client table to be used on this process to delete all information of this client. |
Danger Process
This task executes the same legacy process that you can run in the application like as System Administrator role. It is a very sensitive task you must be very careful because this can lead to crashes in the system if used incorrectly.
A backup previous to executing the task is recommended.
This work is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.5 ES by Futit Services S.L..