Print Provider
Register a new Print Provider
This guide explains how to extend the Print Provider module to integrate an external print provider (e.g., PrintNode, Bartender, Hardware Manager, etc.). The goal is for any module to be able to register its own connector without duplicating common logic and only create buttons pointing to the Send Print Job Action for sending print jobs, which will also automatically resolve the list of available printers and the corresponding print template.
Architecture
The main components of the Print Provider module are:
-
PrintProviderStrategy (Service Provider Interface): Contract to be implemented by each provider. It exposes three operations
-
fetchPrinters(Provider): list of printers (PrinterDTO). -
generateLabel(Provider, Table, recordId, TemplateLine, params): File (PDF). -
sendToPrinter(Provider, Printer, copies, labelFile): String (jobId).
-
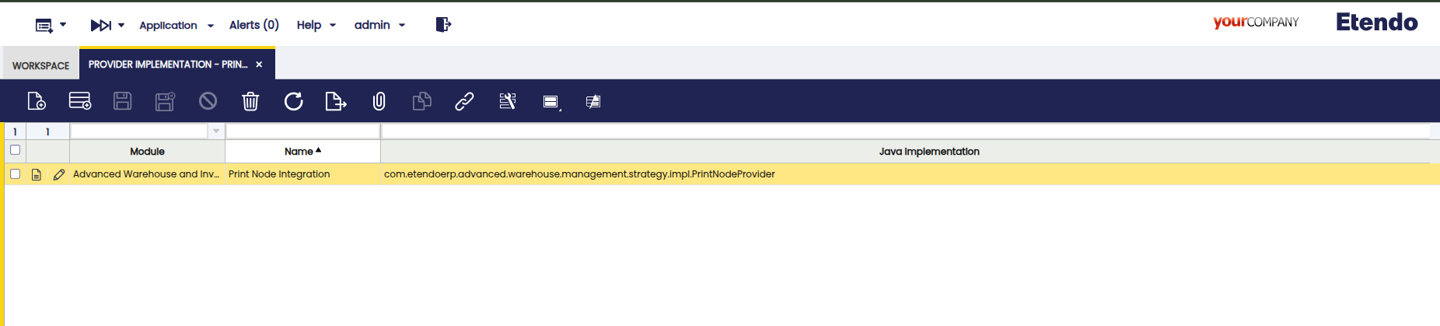
Provider Implementation
General Setup > Print Provider Configuration > Provider Implementation
Info
Access to this window is restricted to users with the System Administrator (Sys) role. Operational users will not be able to modify these settings.
This window allows to register third-party print providers such as PrintNode. Here you can configure credentials, endpoint URLs, and the specific Java implementation that complies with the PrintProviderStrategy contract. Each organization can maintain its own print providers.
Fields to note:
- Module: Indicates the module where the Print Provider configuration will be exported.
- Name: Descriptive name of the provider.
-
Java Implementation: Path to the Java file where the provider implementation is located. This must comply with the established contract, defining how printers are displayed, how the printout is generated, and how it is sent to the printer.
-
Resolve ProviderStrategyResolver: Given a Provider (registered in the Print Providers window), find its ProvidersImplementation (Provider Implementation window), load the class (java Implementation), and return an instance of the strategy.
PrinterUtils utilities: Cross-functional helpers
- Entity loading/validation (requireProvider, requirePrinter, requireTableByName, resolveTemplateLineFor).
- Process/JSON parameters (requireParam, requireJSONArray, requirePositiveInt).
- Provider parameters (getRequiredParam, providerParamContentCheck).
- Jasper templates (resolveTemplateFile, loadOrCompileJasperReport).
- Process result helpers (fail, warning).
-
Actions, ready to use
- UpdatePrinters: synchronizes the supplier's printer catalog (add/update/disable).
- SendGeneratedLabelToPrinter: generates the label (Jasper) and sends it to the selected printer.
-
Key data model
- Provider: Print provider configuration (links implementation, parameters, and printers).
- ProvidersImplementation: Defines the Java class (FQN) of the strategy/SPI to be used by the provider.
- ProviderParam: Provider key/value parameters (e.g., apikey, printersurl, printjoburl).
- Printer: Locally registered printer for a provider (external ID, name, “default,” active).
- Template: Template header associated with a table; groups its lines.
- TemplateLine: Template variant (.jrxml/.jasper path, “default”, order/lineNo).
How to Create a New Supplier
-
Create the strategy class: Create a class in the module that extends
PrintProviderStrategy.MyProviderStrategy.java - Skeleton Examplepublic class MyProviderStrategy extends PrintProviderStrategy { // (optional) constants for timeouts, MIME, etc. @Override public List<PrinterDTO> fetchPrinters(Provider provider) throws PrintProviderException { // 1) Validate provider and required params final ProviderParam printersUrl = PrinterUtils.getRequiredParam(provider, "printersurl"); PrinterUtils.providerParamContentCheck(printersUrl, "printersurl"); // 2) Build HTTP client/request // 3) Send and handle InterruptedException (re-set interrupt + rethrow with context) // 4) Validate statusCode and parse JSON → List<PrinterDTO> // 5) Return list } @Override public File generateLabel(Provider provider, Table table, String recordId, TemplateLine templateRef, JSONObject params) throws PrintProviderException { // Use PrinterUtils.resolveTemplateFile + loadOrCompileJasperReport // Fill report (DOCUMENT_ID, SUBREPORT_DIR) // Export PDF to a temp file and return it } @Override public String sendToPrinter(Provider provider, Printer printer, int numberOfCopies, File labelFile) throws PrintProviderException { // 1) Validate inputs (provider/printer/file) // 2) Read required ProviderParams (e.g., printjoburl, apikey) // 3) Prepare request body (e.g., base64, title, source) // 4) POST; validate response; extract jobId (if available) } @Override public File generateLabel(Provider provider, Table table, String recordId, TemplateLine templateRef, JSONObject params) throws PrintProviderException { // Use PrinterUtils.resolveTemplateFile + loadOrCompileJasperReport // Fill report (DOCUMENT_ID, SUBREPORT_DIR) // Export PDF to a temp file and return it } @Override public String sendToPrinter(Provider provider, Printer printer, int numberOfCopies, File labelFile) throws PrintProviderException { // 1) Validate inputs (provider/printer/file) // 2) Read required ProviderParams (e.g., printjoburl, apikey) // 3) Prepare request body (e.g., base64, title, source) // 4) POST; validate response; extract jobId (if available) } }Contractual conventions
- Printer.value stores the external ID of the printer (key for “upsert”).
- Throw PrintProviderException (extends OBException) for functional/integration failures.
- Do not log secrets (API keys); log context (statusCode, truncated bodies).
-
Register the implementation
-
AD: Provider Implementation
- Java Implementation: com.mi.modulo.print.MyProviderStrategy
-
AD: Print Provider
- Reference to the previous implementation.
-
AD: Provider Param
- Define the keys (reuse if applicable): printersurl, printjoburl, apikey, etc.
- Save values (e.g., your API URLs).
-
How to Register Labels (Jasper)
-
Create a new record in the Print Templates window, indicating the table to which it applies.
-
Indicate the location of your template in the lines tab.
TemplateLine.templateLocationaccepts:- @basedesign@/...
- @
@/... - Paths related to basedesign
Technical Details
- The priority applies to the “Default” check; otherwise, you will get the one with the lowest sequence number.
PrinterUtils.resolveTemplateFileresolves locations insrc-loc/designand web.PrinterUtils.loadOrCompileJasperReportsupports.jrxml(compile) and.jasper(load).
Recommended parameters
- DOCUMENT_ID = recordId
- SUBREPORT_DIR = template directory (for subreports)
Custom Parameter Injection with Hooks
The Print Provider module supports a hook mechanism that allows external modules to inject custom JasperReports parameters during label generation. This capability enables advanced customization scenarios where business logic needs to add or modify report parameters before the report is rendered.
Hook Interface
Modules can implement the GenerateLabelHook interface to customize JasperReports parameters. The hook execution occurs during the generateLabel phase, before the report is filled with data.
Key features:
- Table-specific execution: Each hook declares which tables it applies to via
tablesToWhichItApplies(). - Priority-based ordering: Hooks execute in priority order (lower values first), allowing control over execution sequence.
- Full context access: Hooks receive a
GenerateLabelContextobject providing access to provider configuration, table metadata, record ID, template information, and the parameter map. - CDI integration: Hooks are automatically discovered and managed through CDI.
Implementing a Hook
To create a custom hook:
- Create a class that implements
GenerateLabelHook - Annotate with
@Dependentfor CDI discovery - Implement required methods:
execute(GenerateLabelContext context): Main logic to add/modify parameterstablesToWhichItApplies(): Return list of table IDs where this hook appliesgetPriority()(optional): Return execution priority (default: 100)
Example: Custom Barcode Generation
The following example demonstrates a hook that generates custom barcode labels for business documents. This hook replaces the default database query with a custom data source containing calculated barcode information.
package com.etendoerp.examples.hooks;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.enterprise.context.Dependent;
import com.etendoerp.print.provider.api.GenerateLabelHook;
import com.etendoerp.print.provider.api.PrintProviderException;
import com.etendoerp.print.provider.dto.BarcodeLabelDTO;
import net.sf.jasperreports.engine.data.JRBeanCollectionDataSource;
/**
* Hook that adds custom parameters for document label generation.
* Generates barcode data and provides it as a custom data source.
*/
@Dependent
public class CustomDocumentLabelHook implements GenerateLabelHook {
private static final List<String> TABLES_TO_WHICH_IT_APPLIES = List.of(
"YOUR_DOCUMENT_TABLE_ID", // Document header table ID
"YOUR_DOCUMENT_LINE_TABLE_ID" // Document line table ID
);
@Override
public void execute(GenerateLabelContext context) throws PrintProviderException {
try {
final String recordId = context.getRecordId();
// Retrieve the document record
BaseOBObject currentRecord = getDocumentRecord(recordId);
if (currentRecord == null) {
throw new PrintProviderException("Document not found: " + recordId);
}
// Resolve the lines to process
List<DocumentLine> lines = resolveDocumentLines(currentRecord);
// Generate barcode data for each line
List<BarcodeLabelDTO> barcodeData = generateBarcodeData(lines);
// Create a JRBeanCollectionDataSource with the barcode data
JRBeanCollectionDataSource dataSource = new JRBeanCollectionDataSource(barcodeData);
// Add the datasource as a parameter
// IMPORTANT: This replaces the SQL query in the jasper template
context.addParameter("REPORT_DATA_SOURCE", dataSource);
} catch (PrintProviderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PrintProviderException("Failed to add barcode parameters: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
protected List<BarcodeLabelDTO> generateBarcodeData(List<DocumentLine> lines) {
List<BarcodeLabelDTO> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (DocumentLine line : lines) {
// Build barcode based on business rules (product info, quantities, etc.)
String barcode = buildBarcodeForLine(line);
String barcodeWithSeparator = buildBarcodeWithSeparator(line);
result.add(new BarcodeLabelDTO(barcode, barcodeWithSeparator));
}
return result;
}
@Override
public int getPriority() {
return 50; // Medium priority
}
@Override
public List<String> tablesToWhichItApplies() {
return TABLES_TO_WHICH_IT_APPLIES;
}
}
Hook Context API
The GenerateLabelContext provides the following methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
addParameter(String key, Object value) |
Adds or updates a JasperReports parameter |
getParameter(String key) |
Retrieves the current value of a parameter |
getParameters() |
Returns a read-only view of all parameters |
getProvider() |
Gets the provider configuration |
getTable() |
Gets the target table metadata |
getRecordId() |
Gets the record ID being printed |
getTemplateLine() |
Gets the template line reference |
getJsonParameters() |
Gets the JSON parameters from the request |
Custom Data Sources
Hooks can provide custom data sources by setting the REPORT_DATA_SOURCE parameter. When this parameter is present, the Print Provider will use it instead of the default database connection:
// Create a custom data source from a collection
List<MyDataDTO> data = prepareCustomData();
JRBeanCollectionDataSource dataSource = new JRBeanCollectionDataSource(data);
// Set it as the data source
context.addParameter("REPORT_DATA_SOURCE", dataSource);
This is particularly useful when:
- The data needs complex transformations before rendering
- Data comes from multiple sources (database + external APIs)
- Business logic requires calculated fields not present in the database
- Performance optimization requires pre-aggregated data
Best Practices
-
Error handling: Always wrap business logic in try-catch blocks and throw
PrintProviderExceptionwith meaningful messages. -
Null safety: Validate that required objects are present before accessing them:
if (context.getTable() == null) {
throw new PrintProviderException("Table information is required");
}
-
Recommended priority coordination: Use priority values to control execution order when multiple hooks apply to the same table:
-
System/core hooks: 1-30
- Standard business hooks: 31-70
-
Custom/extension hooks: 71-100
-
Logging: Use SLF4J logging to aid troubleshooting:
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyHook.class);
log.debug("Executing hook for record: {}", recordId);
- Performance: Keep hook execution lightweight. Avoid heavy database queries or external API calls that could slow down label generation.
Printer Update
-
The process calls strategy.fetchPrinters(provider) and performs an upsert on Printer:
- Create if it does not exist (provider, value=externalId).
- Update name/default if it already exists.
- Deactivate printers from the provider that were not included in this synchronization.
-
Printer.value = external ID; Printer.name is user-friendly; Printer.default marks “default.”
Recommendation
If the provider's API does not return a single field that can serve as a stable key, one can be composed (e.g., < accountId >:< remotePrinterId >).
Errors
- Use
PrintProviderExceptionfor exception handling. - Log the messages you need in AD_MESSAGE. You can access these messages using the
String.formatandOBMessageUtils.getI18NMessageformatting utilities.
Workflow and Configuration
Note
Remember that the initial configuration must be performed only once, as the system administrator. Provider parameters such as printersurl and apikey must be defined correctly to avoid connection or printer synchronization failures.
-
Configuration (one-time)
- As System administrator, create a record in Providers Implementation indicating the path of your strategy class.
- As administrator, create a Provider that references the implementation defined in the previous step.
- In the Provider Params tab, define the required parameters (URLs, API key, etc.).
-
Discover Printers
- UpdatePrinters (Action executed from the Printers window): use fetchPrinters from the strategy and synchronize Printer.
-
Generate Label
SendGeneratedLabelToPrinter(Action executed from the button in the desired window) resolves TemplateLine from the table associated with the button window (e.g., button in Product window will resolve table M_Product). This action compiles/loads Jasper and produces the temporary PDF.
-
Send to printer
sendToPrintermakes the necessary HTTP/SDK call and returns jobId (when available).
Basic Example
-
In the module, create
com.my.module.print.MyProviderStrategy(extendsPrintProviderStrategy). -
Configuration per window
-
Provider Implementation:
- specify javaImplementation = com.my.module.print.MyProviderStrategy
-
Print Provider:
- specify the previously registered provider in providers implementation.
-
ProviderParam:
- printersurl: URL for obtaining printers.
- printjoburl: URL for sending print jobs.
- apikey: Key for authenticating with the middleware.
-
-
Run Update Printers from the Printers window. The Action delegates responsibility for updating printers to the fetchPrinters implementation.
-
Execute Generate Printable from the button that has been registered in the desired window. The Action
SendGeneratedLabelToPrinterdelegates the responsibility of:- Generating the printout to your generateLabel implementation.
- Sending the previous print job to your sendToPrinter implementation.
This work is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.5 ES by Futit Services S.L..