How to configure API tokens for Etendo Copilot
Overview
IMPORTANT: THIS IS A BETA VERSION
It is under active development and may contain unstable or incomplete features. Use it at your own risk. The module behavior may change without notice. Do not use it in production environments.
This guide explains how to configure and use API Tokens in Etendo Copilot for secure authentication with external services. API tokens allow agents to authenticate with third-party APIs while maintaining security through proper token management and replacement mechanisms.
What are API Tokens in Etendo Copilot?
API Tokens in Etendo Copilot are secure credentials that allow agents to authenticate with external services and APIs. These tokens are:
- Context-aware: Different tokens can be assigned based on user, role, or global settings
- Prioritized: The system automatically selects the most appropriate token based on context
- Secure: Tokens are stored securely and only exposed during prompt processing
- Flexible: Supports multiple aliases for different services
API Token Priority System
The system implements a sophisticated priority mechanism for token selection:
- User + Role specific: Tokens assigned to both a specific user and role (highest priority)
- User specific: Tokens assigned only to a specific user
- Role specific: Tokens assigned only to a specific role
- Global: Tokens with no user or role assignment (lowest priority)
This ensures that the most contextually appropriate token is always used.
Configuration
Create a New API Token
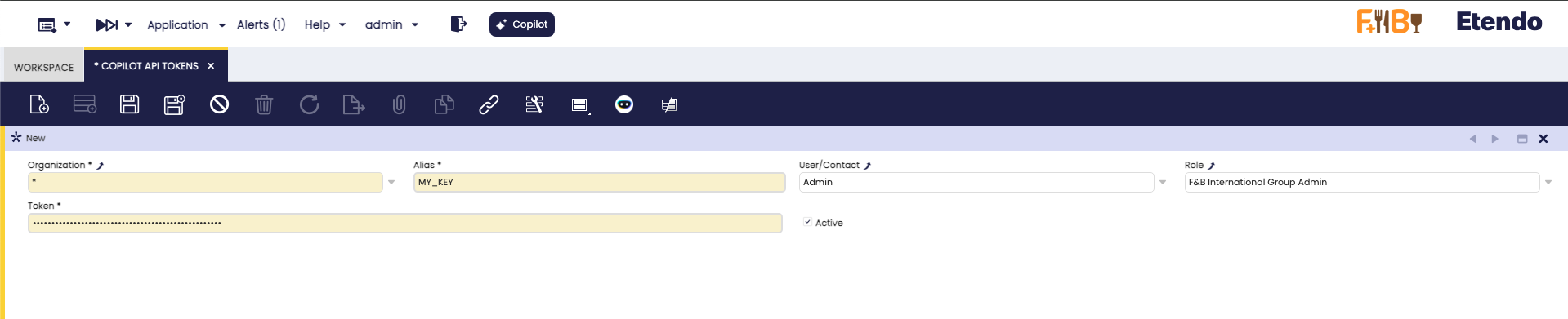
Application > Service > Copilot API Tokens
Etendo must be opened using the role to which the key is to be added. Access is typically restricted to the configuration window for administrators; however, this may vary depending on the access level and configuration assigned to each role.
Create a new record with these fields:
- Organization (Required): The organization that will have access to this token.
- Alias (Required): Name used to reference the token in prompts/configs. Unique name for the token (e.g.,
OPENAI_API,GITHUB_TOKEN). - Token (Required): The API key or token value. (e.g.,
sk-abc123...) - User/Contact (Optional): User with access to the token. Assign to a specific user (leave empty for wider scope).
- Role (Optional): Role allowed to use the token. Assign to a specific role (leave empty for wider scope).
Token Usage in Prompts
Token Placeholder Format
API tokens are referenced in prompts using the following format:
The alias is automatically converted to uppercase for placeholder matching.
Example Usage
In Agent Prompts
Use the OpenAI API with key @OPENAI_API@ to generate a response.
Access GitHub repository using token @GITHUB_TOKEN@.
Connect to Salesforce with @SALESFORCE_API@ credentials.
In Tool Configurations
{
"api_key": "@OPENAI_API@",
"base_url": "https://api.openai.com/v1",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer @OPENAI_API@"
}
}
In MCP Server Authentication
API tokens can be used in MCP server configurations:
{
"command": "npx",
"args": ["custom-mcp-server"],
"env": {
"API_KEY": "@CUSTOM_API@",
"AUTH_TOKEN": "@SERVICE_TOKEN@"
}
}
Token Replacement Process
When prompts are processed, the system:
- Identifies all token placeholders in the format
@ALIAS@ - Evaluates the current user and role context
- Selects the highest priority token for each alias
- Replaces placeholders with actual token values
- Processes the prompt with authenticated credentials
This work is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.5 ES by Futit Services S.L.