How to create a Dataset
Overview
This how-to will focus on creating a dataset in Etendo Classic and also will give some examples in detail under Examples section. Dataset will export both reference data as well as default data.
Introduction to Dataset Concept
First of all we need to understand the dataset concept, which allows to export the sets of data from different tables in one step. This is especially useful to manage and distribute the module along with reference data , for instance tax rates, regions or default data in a new table(s) added by a module.
A dataset is defined by its Dataset Tables and Dataset Columns. This detailed configuration leads to which tables to be exported, and which columns of each table are executed and exported.
There are some important things to note:
- A Dataset belongs to a module, so modules can add Datasets and define their own Datasets.
- Data Access Level: filters the tables which can be selected for this dataset, only tables with the set data access level can be included in the data set.
Reference Data
The reference data is published, distributed and installed together with the program code implementation of the module.
In Etendo, the concept of reference data is generalized and any data in the instance can be exported in a module and imported when installing / applying the module.
Note
You can find the Has reference data field / option at the time of module creation.
Info
For detailed theoretical concepts on datasets please have a look at Datasets.
Data structure to define Dataset
There are mainly three tables referred to as data structure to define datasets. They are:
1. DataSet with the following columns: Value, Name, Description, Module and DataAccessLevel
- Data sets have a name and a description to describe the content of the data set.
- The value is used to get a dataSet object from the factory provided by DAL (eg. DBSourceManager gets the AD dataSet).
- A data set is owned by a module in the same way that all Application Dictionary components.
Note
If the export allowed column is flagged, then an Export Reference Data button is displayed.
2. DataSet_Table with the following columns: DataSet, Table, fullBusinessObject, includeAllColumns, excludeAuditInfo and whereClause (HQL expression)
- A data set can have one or many tables from the ones registered in the
AD_Table. For each of them developers can decide to include only records in that table or export the full business object using the checkfullBusinessObject. - Developers can also define for each table the columns that are included in the dataset. They can include all columns using the
includeAllColumnscheck and then remove some of them in the column definition or only include the ones that are explicitly defined in the column definition. - The whereClause is a HQL expression to filter the rows that are included in the DataSet. Details on this expression will be provided in the DAL project.
- Developers can exclude the audit information column like created, createdby, updated, etc. by checking the
excludeAuditInfocolumn.
Note
If IsBusinessObject field is flagged then the child-records of the table are exported.
For example if the Dataset Table is defined for the C_Order table and this field is flagged then also the related C_OrderLines are exported.
Info
A full business object is a record including all its one-to-many relationships as defined in the AD through the isParent attribute of a column. An example of a full business object is a product with its vendors, prices, etc. A complete description of business objects is provided in the DAL project.
3. Dataset_column with the following columns: DataSet_Table, Column, isExcluded and conditionClause(Java expression).
- For each table in a data set, developers can decide what columns to include from the ones registered in the AD for that table.
- They can exclude columns using the
isExcludedcheck if they have marked the table as Include all columns . Typically audit info will be removed from the dataset.
Data Access Level
The Data Access Level is used to define how to import / install the module at
various levels, like System level, Client level, Organization level, etc. This
access level value is available at Dataset table.
This is a detailed explanation at each access level.
- System Only: data will be imported at module installation time at System level without any user interaction.
- Client: data will be imported at
Initial Client Setupif the user chooses the module where the DataSet is included. - Organization: data will be imported at
Initial Organization Setupif the user chooses the module where the DataSet is included. - Client/Organization: data will be imported at
Initial Client SetuporInitial Organization Setupif the user chooses the module where the DataSet is included. The module can not be applied at both levels at the same time because it would lead to data redundancy. So if the module is applied to a Client it will not be available to apply in its Organizations and if the module is applied in an Organization it will not be available to apply in its Client.
Info
- The relationship between each entry data imported, the DataSet where it came
from, and the original ID it has in the DataSet's XML can be found in
the
AD_Ref_Data_Loadedtable. - Data from a DataSet being imported for the first time will be created with the ID set in its XML file. A new ID will be created for each entry from then on.
- The
AD_Orginfotable has information on which DataSet has ben imported for which client and/or organization
Exporting Module
Before publishing, we need to export the module which creates a directory in the module under Etendo Classic root directory and the appropriate XML files for inclusion in the finished module.
Note
Modules that are not flagged as being in development are not exported, so remember that you must select the InDevelopment checkbox when you define a new module.
When the development of the module is finished, open a command window/shell
and navigate to the Etendo development project, execute the export.database command.
Publishing a Module
The last step in the process is to publish the module and distribute across to the end user.
Info
For a detailed guide on how to do so, visit How to Publish Modules to a GitHub Repository
Examples
Please find below the examples to know how to create a dataset and to export it along with the reference data.
Dataset of roles and accesses
In this section you can find the example of a dataset of roles and access. It basically covers the definition of the role in the organization and the privileges they require.
Create a Role and Assign Privileges
- Change to the admin role of your client.
- Click on
General Setupand Navigate toSecurity>Role. - Create a new record. Fill up the mandatory fields that required for this record. They are:
Name: the name of the role in the customer organization e.i., Sales Clerk, Production Manager, Forecaster, etc.Active: Select Option to ensure this role appears in the generated application. During development you may require the role only to appear when it is complete.User Level: This controls which organizations the role has access to. There are four options, the most common are:Organization: the role only has access to organization specific data.Client and Organization: the role has access to organization specific data and client shared data.
Manual: The controls if all existing privileges are automatically given to the role or if they are manually associated on a peer need basis. Selecting this option for manual control is recommended.
- Save the record.
- Now you need to assign some privileges by clicking on
Grant Accessbutton. - select the module and access type to assign the privileges to the newly created role.
Create a User and assign the user to the Role
- Click on
General Setupand navigate toSecurity>User. - Create a new record. The
Clientfield will show the name of your client by default. - Select the Organization (This can be for access to one or all organizations in a client).
- First Name.
- Last Name.
- Name (Default).
- Select Active (Default).
- Username (The default is a concatenation of first and last name).
- Enter the user Password (Remember this).
-
Save the record.
-
Focus in the
Userwindow again - Select the
User Rolestab. - Create a new record and select a role.
- Save the record.
- Add all roles this new user will be able to have/use (one line for each role).
- Logout from the current role.
Create a new module
- Log into Etendo ERP as a System Administrator.
- Click on
Modulemenu from the Application Dictionary. - From the
Module Typelist, select Module. - In the
Namefield, type the java package name of the module(proper naming convention). - Complete the
DescriptionandHelpfields. Supply the information about chart of accounts. - Select the
Has reference dataoption. - Clear the
Has chart of accounts,Translation requiredandIs translation moduleoptions. - Select the In development option. Remember that you cannot work on a module unless the
In developmentoption is selected. - On the
Dependenciestab, select Core. - Save the module
Create a Dataset of roles and access
- From the Application menu, select
Application Dictionary>Dataset - Click New.
- From the
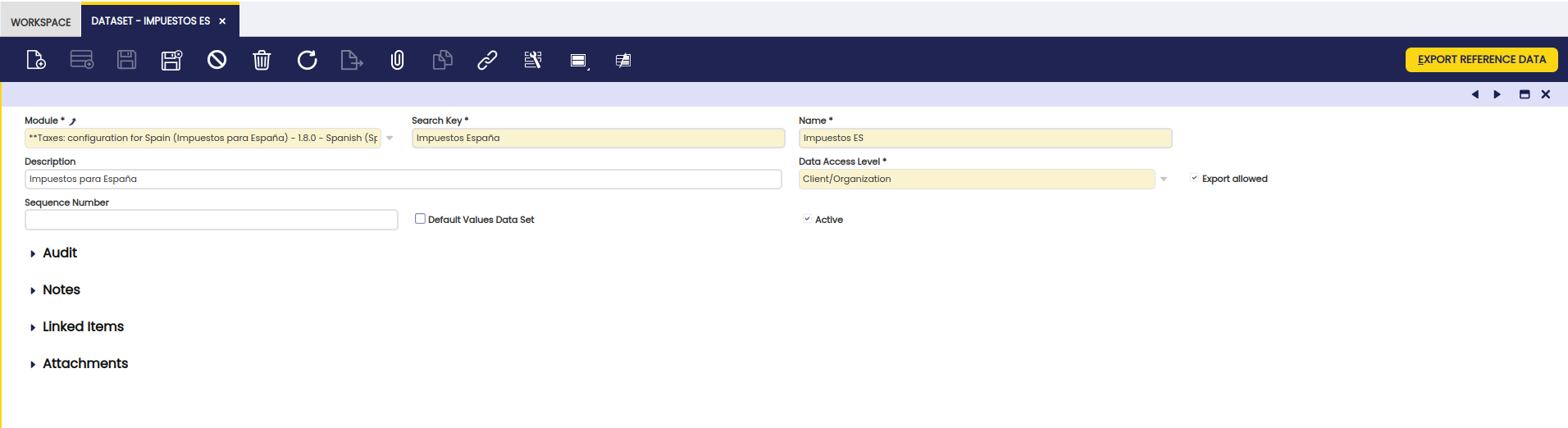
Modulelist, select the module above created. - Specify a search key, name and description.
- From the
Data Access Levellist, select the Data access level as Organization. - Select the
Export allowedoption. - Select the
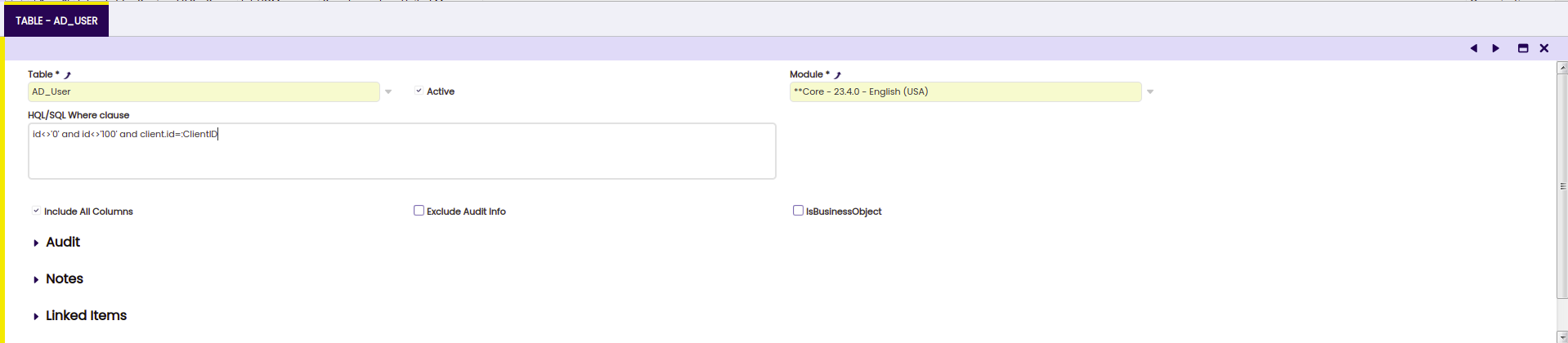
TableTab. - From the
Tablelist, select the table whose content you want to include in the module. For example, ad_role_org_access, ad_role, ad_user_roles. - In the SQL where clause field, specify the SQL "WHERE" statement that will identify the set of rows to be exported, in DAL notation. For example, adrole.id='2EA831D59184490E9BA858E9745EF89F'
- Select the
Include All Columnsoption. - Select
isBusinessObjectoption. - Click Save.
- Click the
Export Reference Databutton to export the reference data to an .xml file that you can include in the module.
Exporting and Publishing Module
After completing all the steps successfully. Run the below gradle task to export the module:
./gradlew export.database
And publish the module.
Info
For more information, see How to Publish Modules to a GitHub Repository.
How to Install - Organization Access Level Reference Data
- Install the module following the Install Modules in Etendo guide.
- At this point the reference data will not be installed.
- Log into the ERP as admin.
- Click on
General Setupand navigate toEnterprise>Enterprise module Management. - Select the
Organization typethen select the appropriate module and click Ok to install the reference data.
Dataset of taxes or alerts
In this section you can find the example on dataset of taxes or alerts. The process for creating a standard reference data module for taxes and alerts, you have set up Etendo ERP in a particular way to meet local requirements, you can export this data and convert it to a module, so that you can share it with other users.
Registering a data module for taxes and alerts:
- Log into Etendo ERP as a System Administrator.
- Click on
Modulemenu from the Application Dictionary. - From the
Module Typelist, select Module. - In the
Namefield, type the java package name of the module(proper naming convention). - Complete the
DescriptionandHelpfields. Supply the information about chart of accounts. - Select the
Has reference dataoption. - Clear the
Has chart of accounts,Translation requiredandIs translation moduleoptions. - Select the
In developmentoption. Remember that you cannot work on a module unless theIn developmentoption is selected. - On the
Dependenciestab, select Core. - Save the module.
Defining and exporting the dataset
- From the Application menu, select
Application Dictionary>Dataset - Click New.
- From the
Modulelist, select the module above created. - Specify a
search key,nameanddescription. - From the
Data Access Levellist, select the Data access level as System only. - Select the
Export allowedoption. - Select the
TableTab. - From the
Tablelist, select the table whose content you want to include in the module. - In the
SQL where clausefield, specify the SQL WHERE statement that will identify the set of rows to be exported, in DAL notation. For example, client.id='1000001' - To export all columns, select the
Include All Columnsoption. To include only the columns you specify, select theColumnstab and create a new record for each column you want to export. - To include the security audit columns (created, createdby, updated and updatedby) in the export, clear the
Exclude Audit Infocheckbox. - Clear the
Is Business Objectoption. - Click Save.
- Click the
Export Reference Databutton to export the reference data to an .xml file that you can include in the module.
Exporting and Publishing Module
After completing all the steps successfully. Run the below gradle task to export the module:
./gradlew export.database
And publish the module.
Info
For more information, see How to Publish Modules to a GitHub Repository.
How to Install - System/Client Access Level Reference Data
- Install the module following the Install Modules in Etendo guide.
- At this point the reference data will not be installed.
- Log into the ERP as admin.
- Click on
General Setupand navigate toClient>Initial Client Setup. - Fill up all the mandatory fields and then select the appropriate module.
- Finally click Ok to install the reference data.
Dataset of regions
In this section you can export the reference data with the examples on regions. Find below the steps to create the Dataset for this module:
- Log into Etendo ERP as a System Administrator.
- Create a new module called Indian States for this example.
- Make sure that you have selected or flagged for the field
Has Reference Data. - Now expand the
Application Dictionarymenu. - Click on
Datasetmenu and create a new record for the for this module. - For example, here the Name
Indian Stateshas been given. You can give a name as you wish to select the region. -
Fill up the Dataset form using the below mentioned values.
Field value for the field Active make it flagged/put a tick mark Module select the value from the drop down Indian States - 1.0.0 Search Key Indian States Name Indian States Data Access Level System Only -
Before assigning the tables to Dataset. Please execute the below query in sqldeveloper or postgres IDE to find the
C_country_Idfor INDIA. After executing the below query the result ofc_country_idwould be 208 for the below query. -
Navigate to
TableTab and create 2 new records for the dataset. -
Fill up the form by using the values below for the following Table:
C_CountryField value for the field Table C_CountryActive Default it is flagged. Leave as it is Module Indian States - 1.0.0 SQL Where Clause id='208' Include All Columns Remove the flag or tick mark (Individual columns will be added in later steps) Exclude Audit Info Mark it as flagged or put tick mark for this check box -
Fill up the form by using the values below for the following Table:
C_RegionField value for the field Table C_RegionActive Default it is flagged. Leave as it is Module Indian States - 1.0.0 SQL Where Clause country.id='208' Include All Columns Mark it as flagged or put tick mark for this check box Exclude Audit Info Mark it as flagged or put tick mark for this check box -
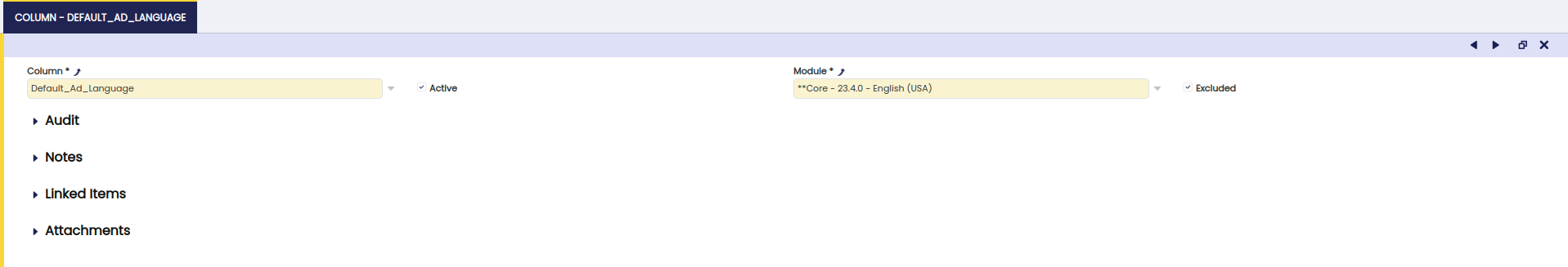
Select the
C_Countrytable from the table grid view and navigate toColumnTab. - Click on create a new record button for the above table. You need to select three columns for this table.
- Those columns are:
- Name
- CountryCode
- HasRegion
-
Fill up the following values in the form.
Field value for the field Column 1: Column Name Active It has benn flagged. Leave as it is Module Indian States - 1.0.0 Column 2: Column CountryCode Active It has benn flagged. Leave as it is Module Indian States - 1.0.0 Column 3: Column HasRegion Active It has benn flagged. Leave as it is Module Indian States - 1.0.0 -
Finally navigate to
Dataset Tabof Indian States and Click onExport Reference Databutton to export the data.
Exporting and Publishing Module
After completing all the steps successfully, run the below gradle task to export the module:
./gradlew export.database
And publish the module.
Info
For more information, see How to Publish Modules to a GitHub Repository.
How to Install - System Only Access Level Reference Data
- Install the module following the Install Modules in Etendo guide.
- It will install along with the reference data.
This work is a derivative of How to Create a Dataset by Openbravo Wiki, used under CC BY-SA 2.5 ES. This work is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.5 by Etendo.