Dockerized Tomcat Service
Javapackage: com.etendoerp.tomcat
Overview
The com.etendoerp.tomcat module enables the Dockerization of Tomcat within Etendo Classic. This module modifies Gradle tasks to automatically deploy the WAR file into the container when executing the smartbuild task.
Info
To be able to include this functionality, the Financial Extensions Bundle must be installed. To do that, follow the instructions from the marketplace: Platform Extensions Bundle. For more information about the available versions, core compatibility and new features, visit Platform Extensions - Release notes.
Configuration Variables
To enable and configure the Tomcat service, the following configuration variables are available:
-
Enable the Service
This variable enables the Tomcat service. -
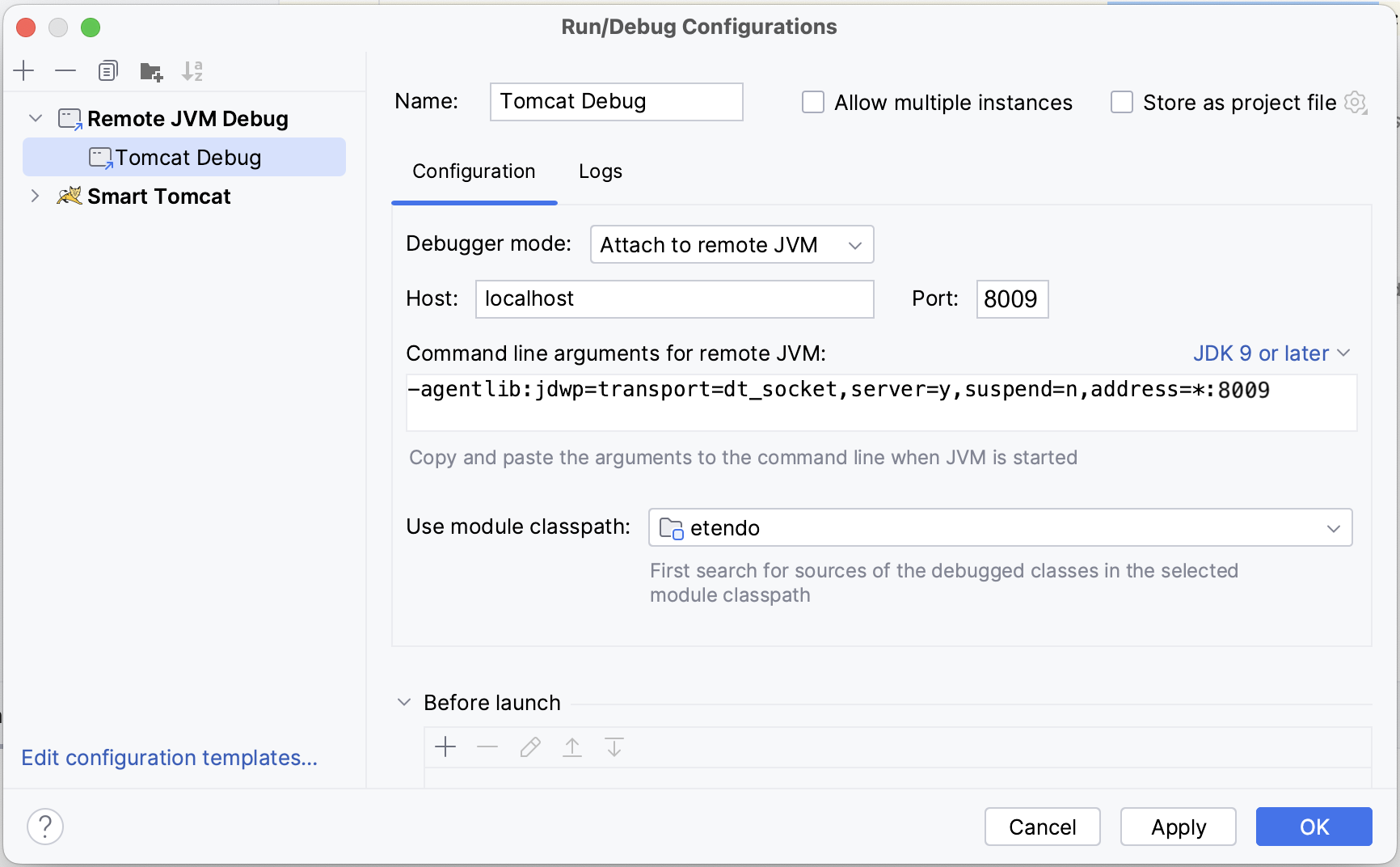
Configure Tomcat Port (Optional)
This variable sets the port for the Tomcat service. The default port is8080 -
Configure Debug Port (Optional)
This variable sets the debug port for the Tomcat service. The default debug port is8009
Execute the following command to apply the configuration changes:
Compile the Environment
-
The first time Tomcat is used within a Docker environment, the setup must be compiled by executing:
This command will update the database and recompile the java classes and deploy the
WARto the dockerized Tomcat service.Info
This module modifies Gradle tasks. Executing the
update.databasecommand will automatically stop the Tomcat service. Thesmartbuildtask will then ensure that theWARfile is correctly deployed in the container. After the smartbuild execution, the service will automatically restart, enabling an automated compilation from the command line. -
Refer to Docker Management page for more information on container management.
Extra Configuration to Use Tomcat (Dockerized) with a Host Database in Linux Environments
-
Listen on the Docker Network
Create the
etendo.conffile in the location/etc/postgresql/<your_pg_version>/main/conf.d/etendo.confwith the following content:Note
The IP address
172.17.0.1is the interface that connects the host with the Docker service. This is the default address used for this connection. -
Allow Access from the Docker Subnetwork
Add the following line to the
/etc/postgresql/<your_pg_version>/main/pg_hba.conffile:Note
The subnet
172.0.0.0/8is used to enable access from Docker Tomcat to the host. By default, Docker assigns a subnet within the range of172.1.0.0/8to172.254.0.0/8.- Restart the PostgreSQL Service
Finally, restart the PostgreSQL service by running the following command in the terminal: