Extended Database Utilities (BETA)
Javapackage: com.etendoerp.db.extended
IMPORTANT:THIS IS A BETA VERSION
- It is under active development and may contain unstable or incomplete features. Use it at your own risk, especially in production environments.
- It should be used with caution, and you should always validate backups before executing any critical operation.
Overview
The Extended Database Utilities module adds advanced PostgreSQL tools to Etendo for managing partitioned tables. Partitioning divides large datasets into smaller segments, improving performance, scalability, and maintainability.
This guide covers requirements, configuration, and usage for partitioning and unpartitioning tables.
Key Features
- Partition and Unpartition PostgreSQL tables
- Manage table structures and metadata
Why Partition?
- Faster queries by scanning only relevant partitions.
- Easier maintenance through logical data organization.
- Scalable growth without degrading performance.
Recommendations
- Always create a full database backup before changes.
- Plan a clear partitioning strategy based on data usage and critical tables.
- Test thoroughly in non-production environments first.
Requirements
The following requirements must be met before using the module:
- Etendo 25 or higher.
- Python 3 – latest release of version 3.
- PostgreSQL – version 16 or higher.
- Etendo DBSM (Database Source Manager) – version 1.2.0-beta, configured in the
artifacts.list.COMPILATION.gradlefile into the Etendo environment.
Installing the module
-
Clone the module code in the
/modulesfolder into the Etendo environment: -
Compile the environment.
Setting up the Python Environment
To prepare the Python environment necessary for this module:
-
Create a virtual environment:
-
Activate the virtual environment:
-
Install the required Python packages:
Partition a Table
Partitioning a table alters its physical structure to improve query performance for very large datasets. This process must be executed cautiously and requires appropriate permissions.
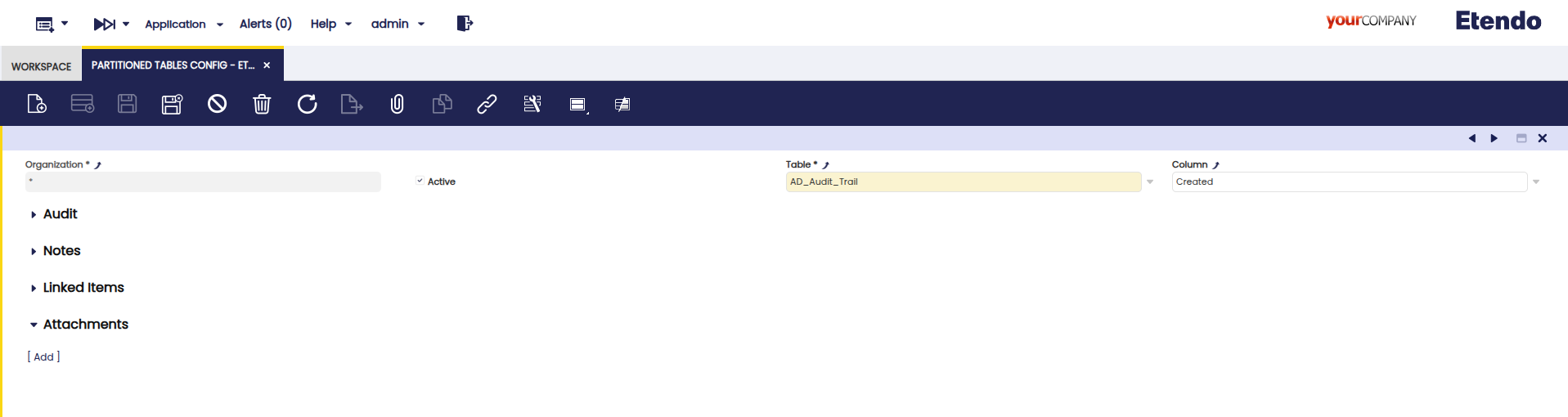
Partitioned Table Config Window
Application> Partition> Partitioned Table Config
- Log in as System Administrator.
- Access the Partitioned Table Config Window.
-
Define how tables should be partitioned:
- Create a new configuration record.
- Select the table you wish to partition.
-
Choose a column for partitioning (must reference a date).
Why a date reference?
This is because the partitioning script uses the selected column to extract the year from each record and then groups the data into partitions based on that year. Therefore, the column must have a date reference.
-
Save the configuration.
Apply the Partitioning
- Stop the Tomcat server.
-
Execute the following commands to partition the table(s):
Terminalpython3 modules/com.etendoerp.db.extended/tool/migrate.py ./gradlew update.database -Dforce=yes smartbuild- The first command executes the partitioning process based on the configuration set in the data dictionary.
-
The second command updates the database by regenerating the table structures to reflect the partitioning.
Note
A forced
update.databaseis executed here because, after partitioning a table, the database structure changes due to one or more tables being partitioned. This step ensures that the updated structure is correctly applied, including handling of partitioned tables, which the default DB Source Manager would not manage properly.
Unpartition a Table
Before starting development, tables must be unpartitioned because the export.database task does not support partitioned tables.
The unpartitioning tool restores tables to their original, non-partitioned state, ensuring compatibility with development workflows.
Warning
The export.database task cannot be executed on partitioned tables. Always unpartition the required tables before running this task.
Steps to Unpartition a Table
-
Execute the following command, replacing "table_name1", "table_name2", etc., with the name of the table(s) you want to unpartition.
Info
It's possible to unpartition one or multiple tables by listing their names separated by commas (no spaces between names).
Example:
-
Unpartition a single table:
-
Unpartition multiple tables:
-
-
Regenerate the Database Structure:
After unpartitioning, run the following command to update the database metadata:
This step restores the database to a consistent and functional state by reflecting the changes made during the unpartitioning process.
This module is in BETA Phase
The module behavior may change without notice. Do not use it in production environments without thorough validation.
This work is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.5 ES by Futit Services S.L..