Subapplications Structure in Etendo Mobile
Overview
This page provides a comprehensive guide to the structure of subapplications in Etendo Mobile. It explains key concepts such as the App.tsx file, which serves as the main entry point for subapplications, and details how parameters from Etendo Mobile are utilized for initialization. Additionally, the guide covers language management, navigation between screens using the navigation stack, and the use of the Etendo UI Library for consistent design and functionality across subapps. These elements form the foundation for developing dynamic and well-integrated subapplications within Etendo Mobile.
App File
In App.tsx, it is the main file located in the root of the subapplication. In this file, we will define the routes and the components that will be rendered in each route. In addition, this file is responsible for the initialization of the subapplication and gets the params from Etendo Mobile.
Params from Etendo Mobile
Etendo Mobile sends params to the subapplication and all of them are ready to use, they are:
Params
- _ id: ID of the subapplication
- url: the environment URL(setted in setting's Etendo Mobile)
- _contextPathUrl: the environment context path (setted in setting's Etendo Mobile)
- navigationContainer: an instance of the navigation container of Etendo Mobile
- token: Token
- language: Language
- dataUser: all data related to the user. It has a typed interface that can be found in the file
src/interfaces/index.ts - isDev: boolean that identifies whether the application is configured in development (true) or production (false) mode.
- Camera: a component previously integrated into Etendo Mobile has now been seamlessly transferred to the subapps. This particular component includes a remarkable QR code scanning capability, enhancing the overall functionality of the subapps.
- sharedFiles: IFile array, if a file is shared to Etendo Mobile from an external application, sharing and selecting a sub-application will add the file to the file array of the corresponding sub-application.
Language
The language is a string that serves as a representation of the user's selected language. This language setting is configurable within the Etendo Mobile application's settings and plays a crucial role in determining the language in which texts are presented within the subapplication. In this example, we will use the language parameter received as input to initialize the remaining aspects of the application in the App.tsx file.
Tip
All subapps must be developed in English en-US and may include translations such as Spanish es-ES.
As you can see, we use locale to set the language of the subapplication. This locale is an instance of a custom handler of the language which is based in i18n and defined in the path subapp/src/localization/locale.ts.
const locale: LocaleModule = {
currentDateLocale: null,
i18n,
init() {...}
t(key, params) {...}
setCurrentLanguage(input) {...}
};
export default locale;
Info
- Translations folder: Translations are organized in the folder
subapp/src/lang - JSON files by language: Each translation file corresponds to a language and locale, following a structure that includes the language code and region. E.g:
Between the functions of the locale handler, some of the most important are:
-
t(key, params): this function receives a key (and other optional params) and returns the text translated to the language of the subapplication. This function is based on i18n and the keys are defined in.jsonfiles insubapp/src/lang. -
setCurrentLanguage(input): gets a language as a param and sets this language as default in the subapplication.
The translation definition files can group the information, for example, in the English translations file /subapp/src/lang/enUS.json we can group the messages or labels by screens, components or as it is optimal according to the development. For Example
{
"ScreenOne": {
"LabelOne": "Label 1 Example",
"LabelTwo": "Label 2 Example",
},
"ScreenTwo": {
"LabelOne": "Label 1 Example",
"LabelTwo": "Label 2 Example",
},
Then to use it, use the local.t function, E.g: locale.t('ScreenOne.LabelOne')
Navigation Stack
The navigation stack part of App.tsx that allows us to navigate between screens. It is a component provided by @react-navigation/stack in a React Native application. Conceptually, a navigation stack manages the flow between different screens in the app, allowing users to navigate forward and backward between these screens.
Key Concepts
-
Navigation Stack Initialization:
ThecreateStackNavigator()function from@react-navigation/stackis used to create a navigation stack. This stack manages a sequence of screens, and each screen is treated as a "route" within the stack. -
Screen Definitions: Each screen in the app is defined using the
Stack.Screencomponent. Thenameprop specifies the unique identifier of the screen, and the component associated with the screen is defined within the children or passed as a function using render props ({props => <Component {...props} />}).Example of screen definitions:
-
Initial Route: The
initialRouteNameprop inStack.Navigatorspecifies which screen will be loaded first when the app starts. In the following example case, the Home screen is defined as the initial route:
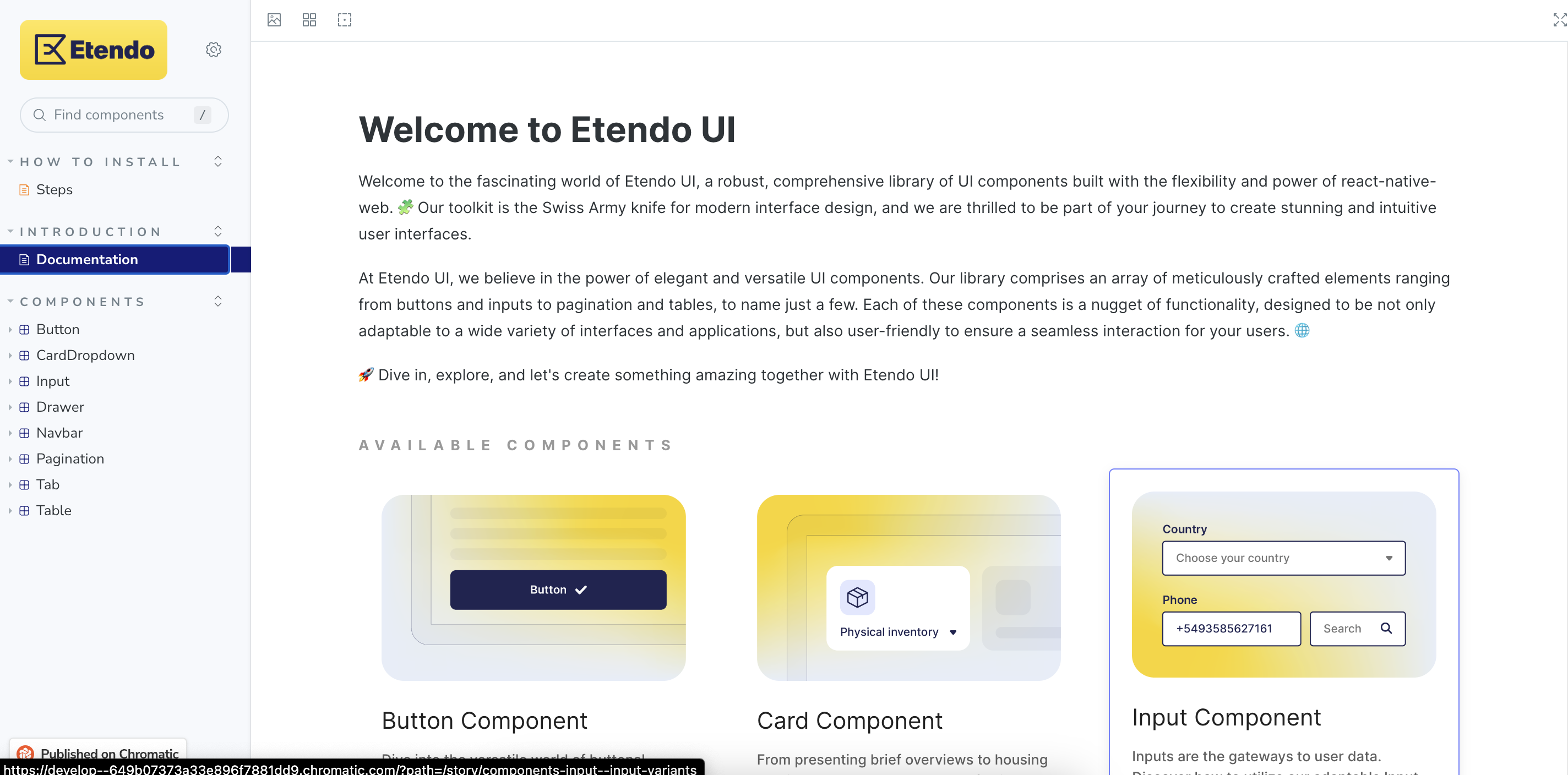
Etendo UI Library
Etendo UI Library is a library of UI components following the style and design of Etendo, that should be used throughout the subapplication development. This library is based on React Native Elements and it is available on NPM - Etendo UI Library . You can use it in all of your subapplications. In this library, we can find components like: Button, Input, Navbar, Cards, Icons, etc.
Info
For more information, visit Etendo UI Library - Storybook place where you can see all the components of the library. Also, you can see the code of each component and how to use it.